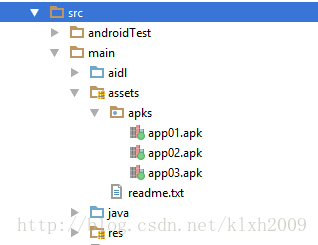
1.复制Assets文件到手机SD卡
assets文件夹里面的文件都是保持原始的文件格式,需要用AssetManager以字节流的形式读取文件。
- 先在Activity里面调用
getAssets()来获取AssetManager引用; - 再用AssetManager的
open(String fileName, int accessMode)方法则指定读取的文件以及访问模式就能得到输入流InputStream; - 然后就是用已经open file 的
inputStream读取文件,读取完成后记得inputStream.close(); - 调用
AssetManager.close()关闭AssetManager。 封装类实现FileUtils类,代码遵循单例模式
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Looper;
import android.os.Message;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class FileUtils {
private static FileUtils instance;
private static final int SUCCESS = 1;
private static final int FAILED = 0;
private Context context;
private FileOperateCallback callback;
private volatile boolean isSuccess;
private String errorStr;
public static FileUtils getInstance(Context context) {
if (instance == null)
instance = new FileUtils(context);
return instance;
}
private FileUtils(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
private Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
if (callback != null) {
if (msg.what == SUCCESS) {
callback.onSuccess();
}
if (msg.what == FAILED) {
callback.onFailed(msg.obj.toString());
}
}
}
};
public FileUtils copyAssetsToSD(final String srcPath, final String sdPath) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
copyAssetsToDst(context, srcPath, sdPath);
if (isSuccess)
handler.obtainMessage(SUCCESS).sendToTarget();
else
handler.obtainMessage(FAILED, errorStr).sendToTarget();
}
}).start();
return this;
}
public void setFileOperateCallback(FileOperateCallback callback) {
this.callback = callback;
}
private void copyAssetsToDst(Context context, String srcPath, String dstPath) {
try {
String fileNames[] = context.getAssets().list(srcPath);
if (fileNames.length > 0) {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), dstPath);
if (!file.exists()) file.mkdirs();
for (String fileName : fileNames) {
if (!srcPath.equals("")) { // assets 文件夹下的目录
copyAssetsToDst(context, srcPath + File.separator + fileName, dstPath + File.separator + fileName);
} else { // assets 文件夹
copyAssetsToDst(context, fileName, dstPath + File.separator + fileName);
}
}
} else {
File outFile = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), dstPath);
InputStream is = context.getAssets().open(srcPath);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int byteCount;
while ((byteCount = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0, byteCount);
}
fos.flush();
is.close();
fos.close();
}
isSuccess = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
errorStr = e.getMessage();
isSuccess = false;
}
}
public interface FileOperateCallback {
void onSuccess();
void onFailed(String error);
}
}
调用代码实现文件复制: 如果你需要将如图所示的apks下的文件复制到SD卡的app/apks目录下,则这样调用:
FileUtils.getInstance(Context context).copyAssetsToSD("apks","app/apks"); 如果你需要收到文件复制完成的时的回调,则使用如下代码
如果你需要收到文件复制完成的时的回调,则使用如下代码
FileUtils.getInstance(Context context).copyAssetsToSD("apks","app/apks").setFileOperateCallback(new FileUtils.FileOperateCallback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
// TODO: 文件复制成功时,主线程回调
}
@Override
public void onFailed(String error) {
// TODO: 文件复制失败时,主线程回调
}
});代码说明 在上面代码中,通过单例模式传入一个context获得FileUtils实例,通过实例去调用copyAssetsToSD()方法,方法参数:
String srcPath 传入assets文件夹下的某个文件夹名,如上述apks,可传入为空”“字符,则复制到SD后,默认将assets文件夹下所有文件复制;
String sdPath 传入你希望将文件复制到的位置,如SD卡下的“abc”文件夹,则传入”abc”
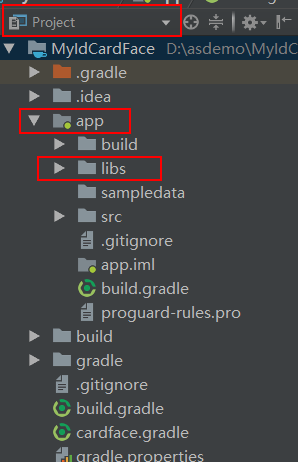
2.Androidstudio中添加jar包的方法
先到网上下载你需要的jar包,下载下来后,将你Androidstudio中的项目切换为project,找到app下的libs,将你下载的jar包复制粘贴进去
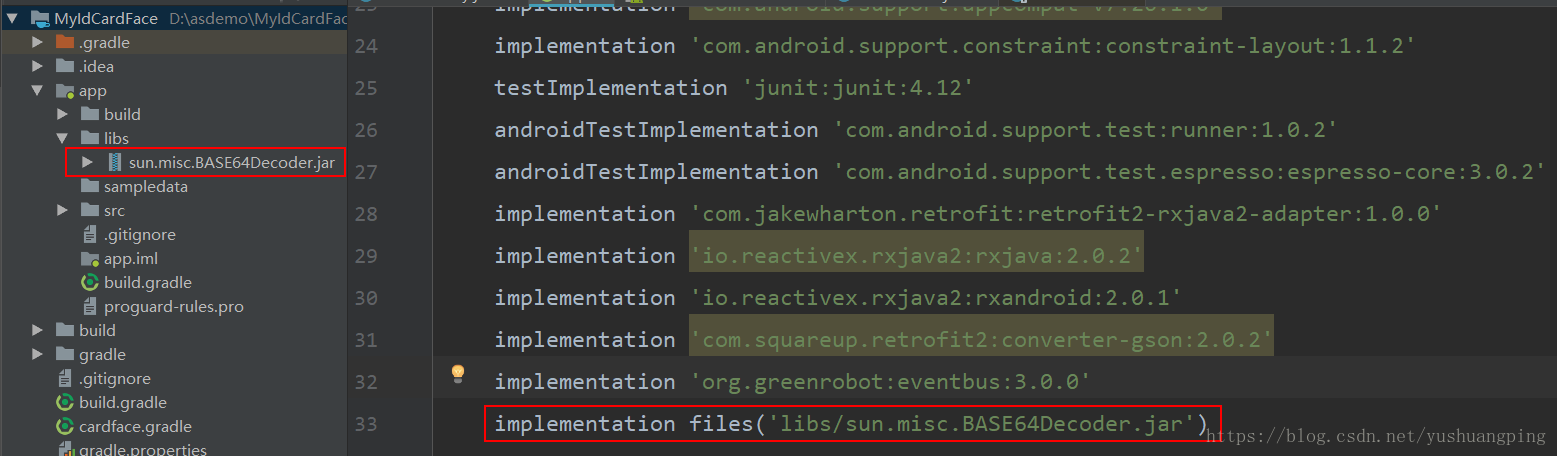
 jar包复制进去后,选中你的jar包,比如这里放了一个sun.misc.BASE64Decoder的jar包进去,选中sun.misc.BASE64Decoder,右键,选择add as library,放进你的module中(要是有多个module,要注意自己要放进哪个module),然后加载下就可以了,下图所示,说明jar包添加成功:
jar包复制进去后,选中你的jar包,比如这里放了一个sun.misc.BASE64Decoder的jar包进去,选中sun.misc.BASE64Decoder,右键,选择add as library,放进你的module中(要是有多个module,要注意自己要放进哪个module),然后加载下就可以了,下图所示,说明jar包添加成功:
3.在Android Project种编写并独立运行测试纯Java代码
方法一:通过Java Library实现
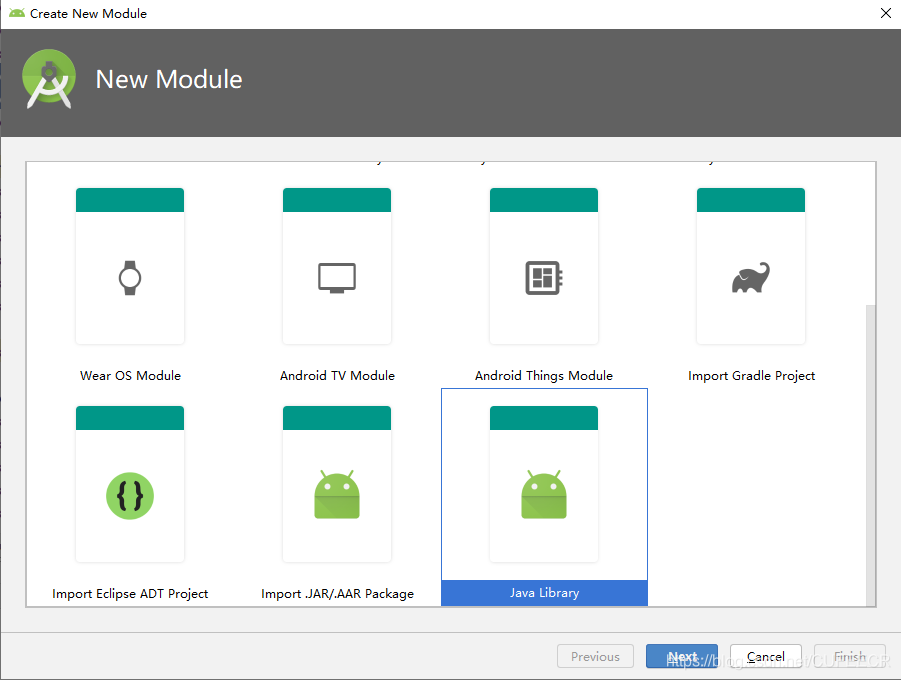
(1)新建
File-->New-->New Module-->Java Library-->Next-->Finish,此步骤最重要是选择Java Library,请注意选择,有可能你需要下拉到最底下才能找到,如图:
 (2)代码示例
(2)代码示例
package com.baidu.tts.javalib;
public class JavaTest {
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello World!!!");
}
}
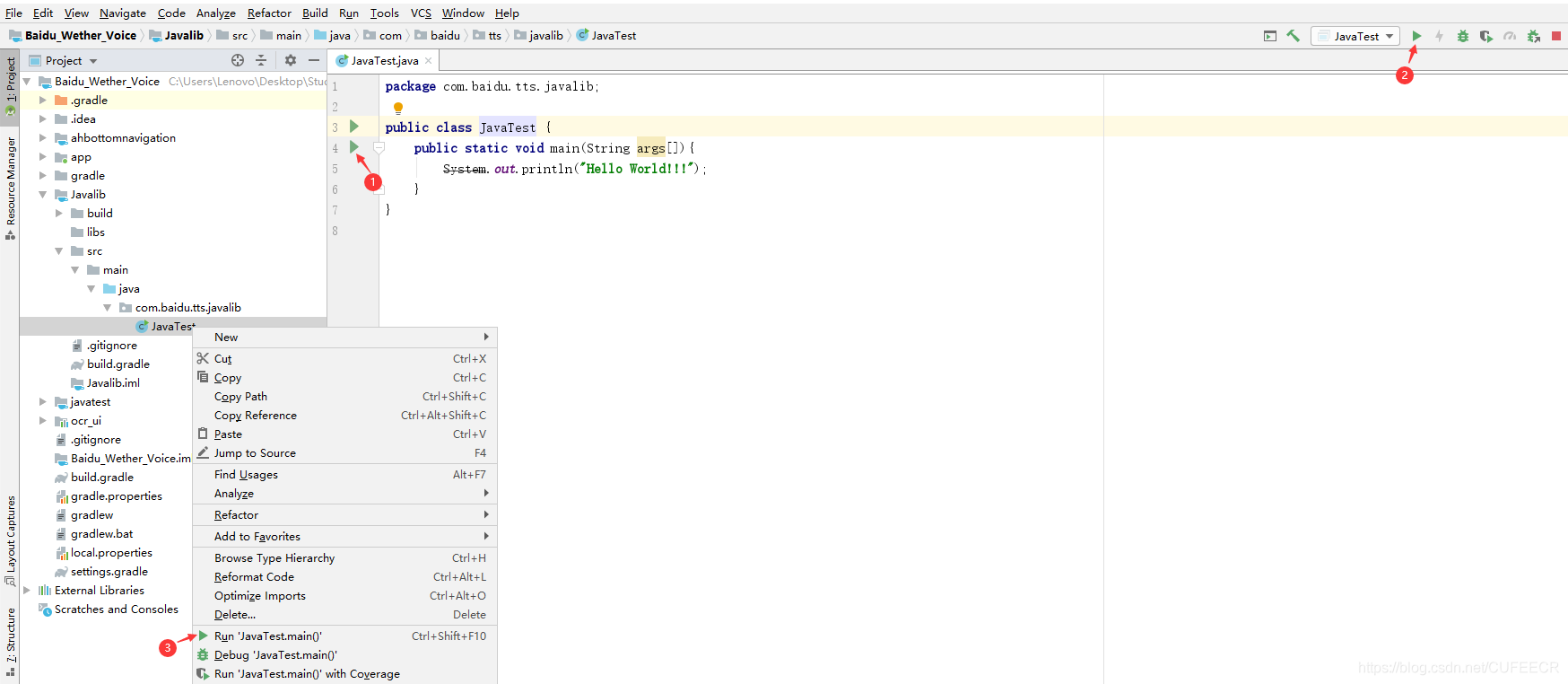
(3)运行
常用的运行方法有三种:
①直接点击函数右边三角符号;
②在.java文件上右键,选择Run;
③点击工具栏上的三角符号。
如下图所示
方法二:通过单元测试实现
单元测试中有一个本地测试(Local Tests)可实现此功能。
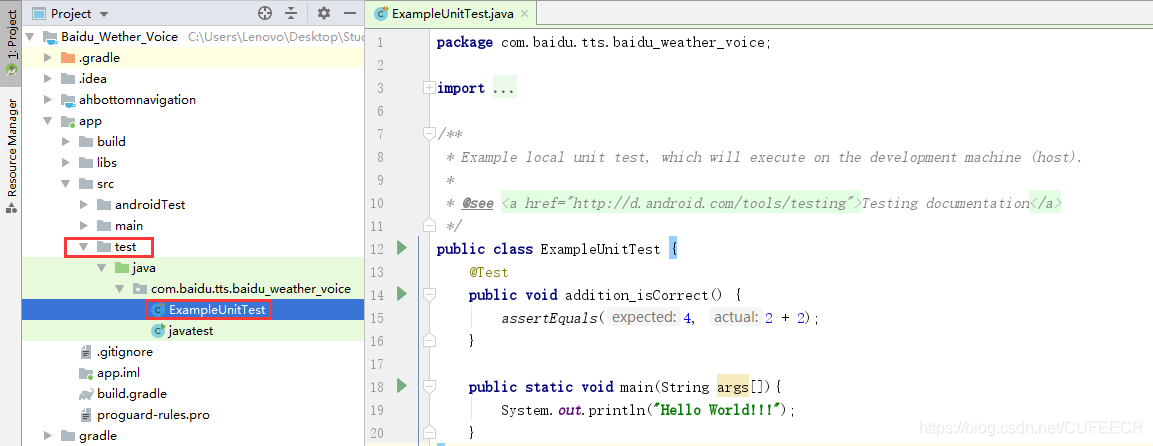
(1)新建
Android Studio创建项目的时候会自动创建一个test文件夹,如图。
 (2)代码示例
(2)代码示例
public class ExampleUnitTest {
@Test
public void addition_isCorrect() {
assertEquals(4, 2 + 2);
}
public static void main(String args[]){
System.out.println("Hello World!!!");
}
}
(3)运行 同方法一。 ※推荐使用方法2,Android Studio自带,不会污染代码。
4.在EditText中软键盘的调起、关闭
(1)EditText有焦点(focusable为true)阻止输入法弹出
editText.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener(){
public boolean onTouch(View view,MotionEvent event){
editText.setInputType(Input.TYPE_NULL);//关闭软键盘
return false;
}});(2)EditText无焦点(focusable=false)时阻挡输入法弹出
public static void hideInputManager(Context context,View view){
InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) context.getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE);
if (view !=null && imm != null){
imm.hideSoftInputFromWindow(view.getWindowToken(), 0); //强制隐藏
}
}(3)键盘永远不会弹出
android:focusable="false"// 键盘永不弹出5.禁止EditText自动弹出软键盘
(1)在包含EditText的父布局中添加android:focusable="true"和android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:focusable="true"
android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:inputType="text"
android:maxLines="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
(2)在AndroidManifest.xml中添加stateHidden
<activity android:name=".TestAActivity"
android:windowSoftInputMode="adjustResize|stateHidden">
</activity>(3)进入页面强制隐藏软键盘 如果前两种方法都不起作用的话,可以使用这种方法:
/**
* 隐藏输入软键盘
* @param context
* @param view
*/
public static void hideInputManager(Context context,View view){
InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager) context.getSystemService(Context.INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE);
if (view !=null && imm != null){
imm.hideSoftInputFromWindow(view.getWindowToken(), 0); //强制隐藏
}
}6.EditText输入文本从右边开始显示
在进行计算器等开发的时候,常常需要在EditText控件输入的文本从右边开始显示:
在xml文件中加入android:gravity="right"或者android:gravity="end"。
7.判断APP是否联网
首先要做的是在manifest中添加权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>然后判断:
ConnectivityManager cwjManager=(ConnectivityManager)getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
NetworkInfo info = cwjManager.getActiveNetworkInfo();
if (info != null && info.isAvailable()){
//you want do eveything!
}
else
{
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"无互联网连接",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}8.检查网络连接状态的变化无网络时跳转到设置界面
在AndroidManifest.xml中加一个权限:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE" />
</intent-filter>主代码中实现:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
checkNetwork();
if (!checkNetwork()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "没有网络", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
Intent intent = new Intent("android.settings.WIRELESS_SETTINGS");
startActivity(intent);
return;
}
}
private boolean checkNetwork() {
ConnectivityManager conn = (ConnectivityManager) getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
NetworkInfo net = conn.getActiveNetworkInfo();
if (net != null && net.isConnected()) {
return true;
}
return false;
}9.复制Assets文件到SD卡
原理: (1)先在Activity里面调用getAssets() 来获取AssetManager引用。 (2)再用AssetManager的open(String fileName, int accessMode) 方法则指定读取的文件以及访问模式就能得到输入流InputStream。 (3)然后就是用已经open file 的inputStream读取文件,读取完成后记得inputStream.close() 。 (4)调用AssetManager.close() 关闭AssetManager。 代码:
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Looper;
import android.os.Message;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class FileUtils {
private static FileUtils instance;
private static final int SUCCESS = 1;
private static final int FAILED = 0;
private Context context;
private FileOperateCallback callback;
private volatile boolean isSuccess;
private String errorStr;
public static FileUtils getInstance(Context context) {
if (instance == null)
instance = new FileUtils(context);
return instance;
}
private FileUtils(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
private Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
if (callback != null) {
if (msg.what == SUCCESS) {
callback.onSuccess();
}
if (msg.what == FAILED) {
callback.onFailed(msg.obj.toString());
}
}
}
};
public FileUtils copyAssetsToSD(final String srcPath, final String sdPath) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
copyAssetsToDst(context, srcPath, sdPath);
if (isSuccess)
handler.obtainMessage(SUCCESS).sendToTarget();
else
handler.obtainMessage(FAILED, errorStr).sendToTarget();
}
}).start();
return this;
}
public void setFileOperateCallback(FileOperateCallback callback) {
this.callback = callback;
}
private void copyAssetsToDst(Context context, String srcPath, String dstPath) {
try {
String fileNames[] = context.getAssets().list(srcPath);
if (fileNames.length > 0) {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), dstPath);
if (!file.exists()) file.mkdirs();
for (String fileName : fileNames) {
if (!srcPath.equals("")) { // assets 文件夹下的目录
copyAssetsToDst(context, srcPath + File.separator + fileName, dstPath + File.separator + fileName);
} else { // assets 文件夹
copyAssetsToDst(context, fileName, dstPath + File.separator + fileName);
}
}
} else {
File outFile = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory(), dstPath);
InputStream is = context.getAssets().open(srcPath);
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outFile);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int byteCount;
while ((byteCount = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0, byteCount);
}
fos.flush();
is.close();
fos.close();
}
isSuccess = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
errorStr = e.getMessage();
isSuccess = false;
}
}
public interface FileOperateCallback {
void onSuccess();
void onFailed(String error);
}
}
可参考https://blog.csdn.net/klxh2009/article/details/55191409。
10.从当前APP跳转到其他应用
(1)为目标APP的目标Activity添加权限属性(让其它应用拥有启动它的权限)
<activity android:name=".SplashActivity" android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.demo"/>
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT"/> (不加此行会崩溃报错)
</intent-filter>
</activity>(2)进行跳转 方式一:
/**
* App内跳转其它应用某activity的第一种方式
*/
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("android.intent.action.demo");
startActivity(intent);方式二:
/**
* App内跳转其它应用某activity的第二种方式
*/
ComponentName componetName = new ComponentName(
"com.example.life", //这个是另外一个应用程序的包名
"com.example.life.SplashActivity"); //这个参数是要启动的Activity的全路径名
try {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(componetName);
startActivity(intent);
} catch (Exception e) {
Toast.makeText(this, "跳转异常,请检查跳转配置、包名及Activity访问权限", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}注意事项:
无论方式一还是方式二,都必须给目标activity注册标签中加入 android:exported="true"属性;
在不清楚目标包名 以及 目标Activity的完整路径时,建议使用 代码第一种方式,即 使用 action 启动,但是不要忘记在目标App的Activity注册时,添加对应的action和category ;
如果知晓目标APP的包名以及目标Activity路径,这种情况就建议使用第二种方式,这种方式就无需在目标Activity注册的标签中加入action 和 category标签了。
可参考https://blog.csdn.net/xyl826/article/details/88555585。
本文原文首发来自博客专栏移动应用开发,由本人转发至https://www.helloworld.net/p/Z1Xi0Lu7wuzB,其他平台均属侵权,可点击https://blog.csdn.net/CUFEECR/article/details/103489522查看原文,也可点击https://blog.csdn.net/CUFEECR浏览更多优质原创内容。