Java BIO、NIO与AIO的介绍
因为netty是一个NIO的框架,所以在学习netty的过程中,开始之前。针对于BIO,NIO,AIO进行一个完整的学习。
学习资源分享:
Netty学习:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1DJ411m7NR?from=search&seid=8747534277052777648
Netty源码:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1cb411F7En?from=search&seid=12891183478905555151
数据结构和算法:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1E4411H73v?from=search&seid=9508506178445014356
java设计模式:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1G4411c7N4?from=search&seid=9508506178445014356
以上资源,均来源于网友发布在Bilibili的数据。
Java BIO编程
BIO - 阻塞IO。 即Java的远程IO
IO模型

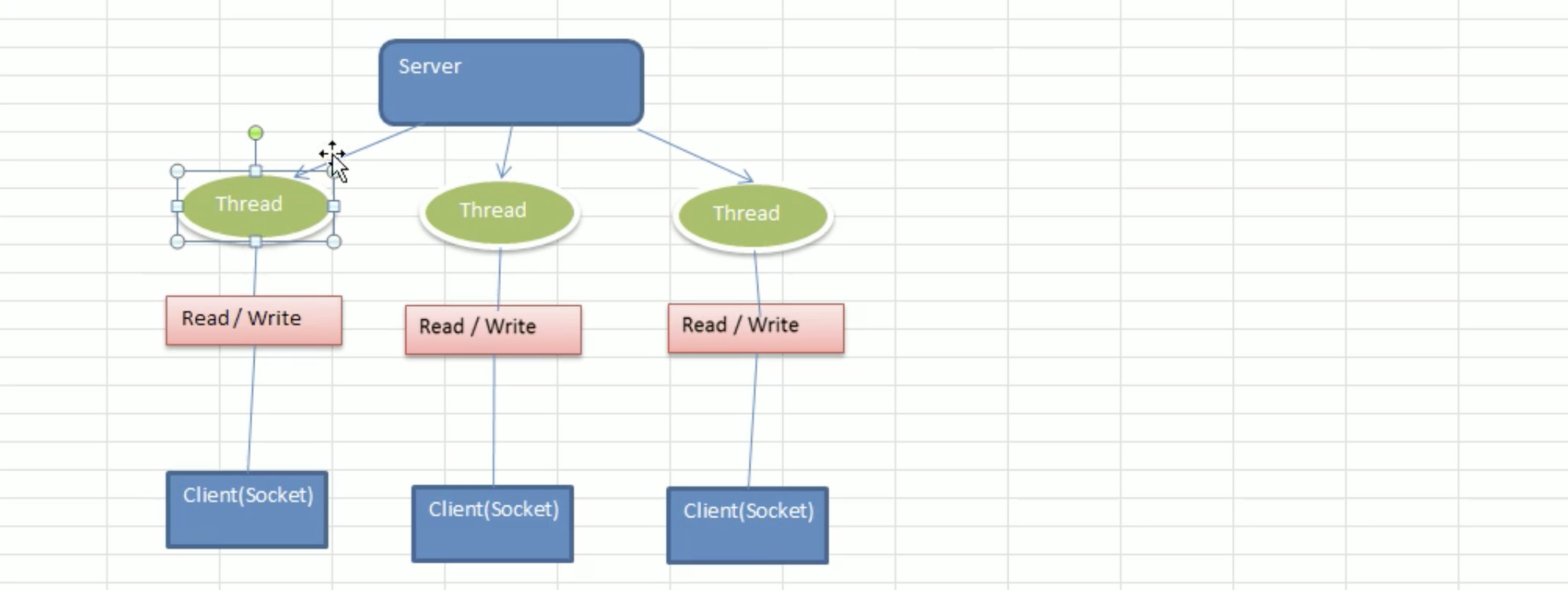
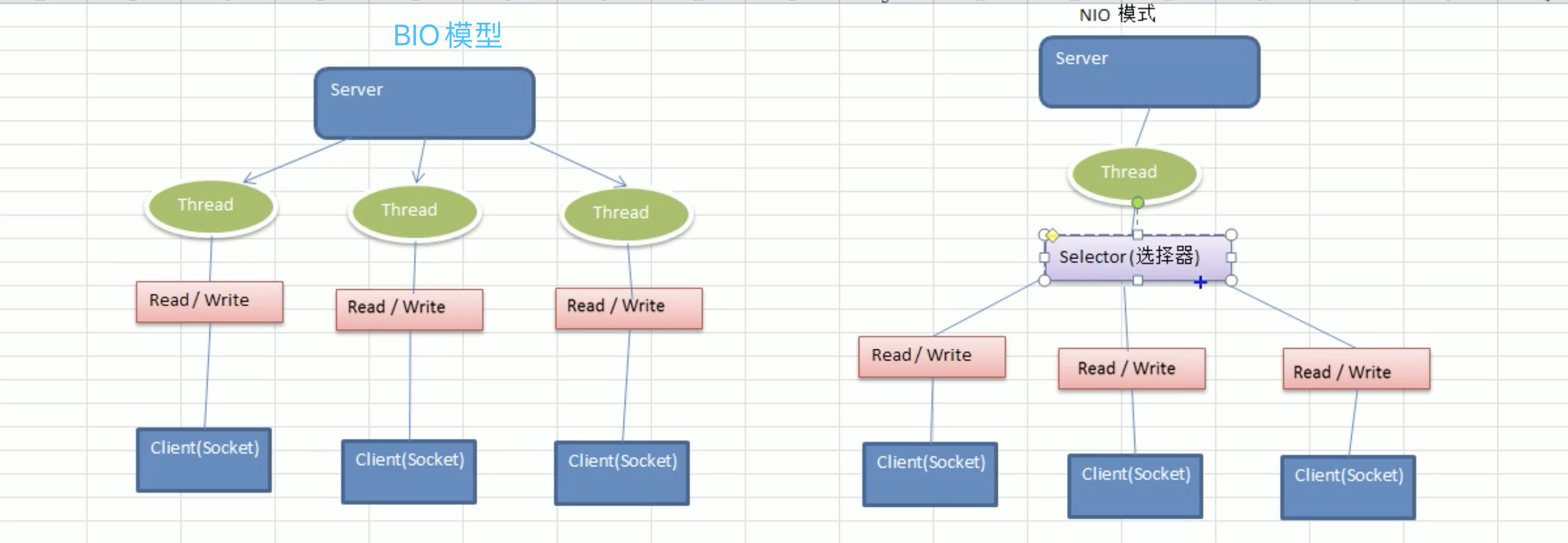
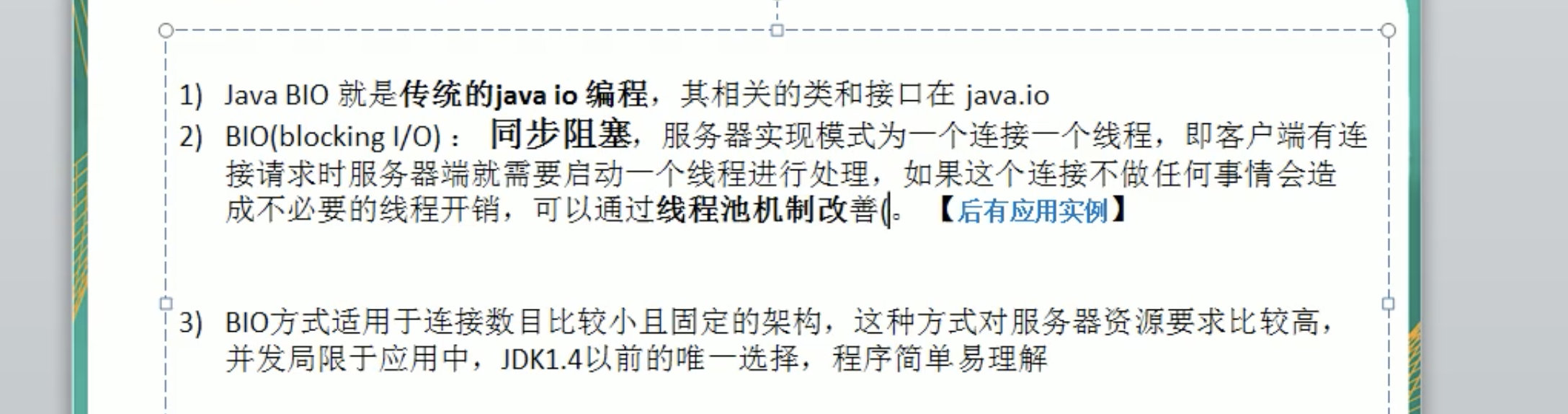
BIO线程模型:
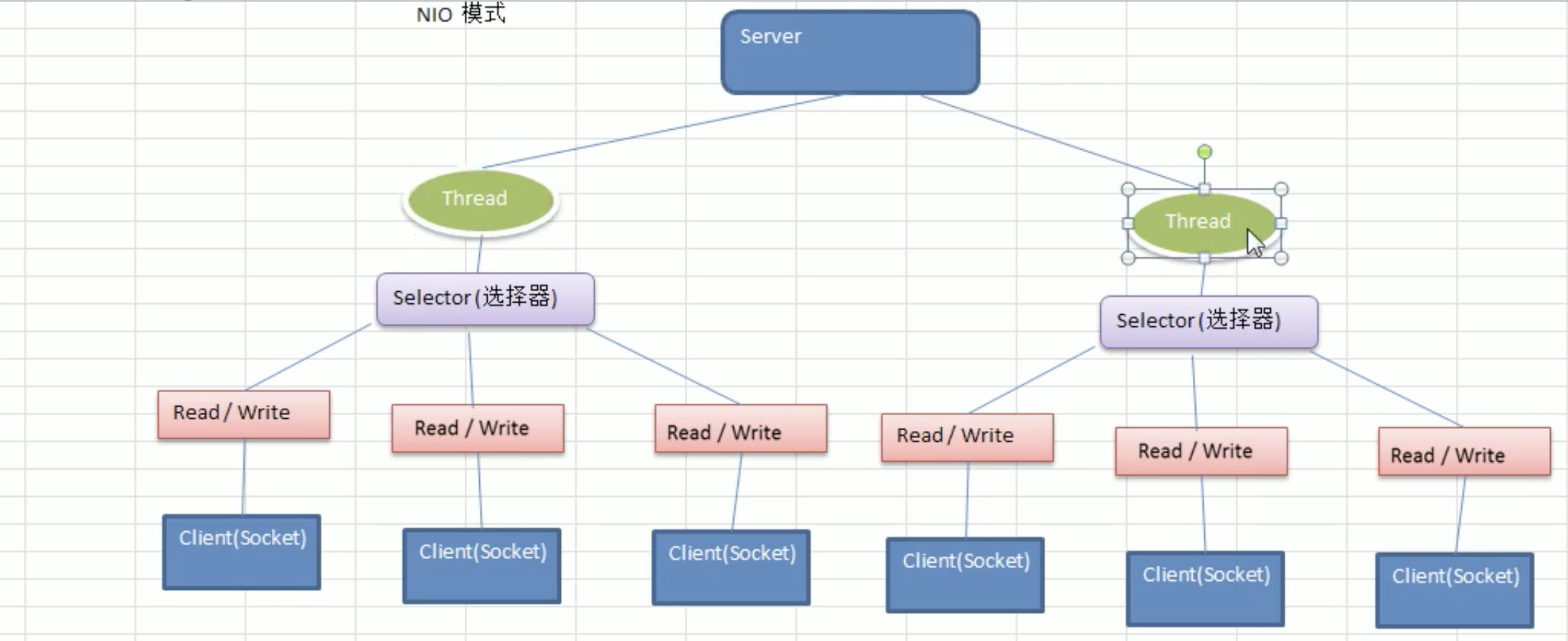
NIO模型(简单描述):
IO模型应用场景

Java BIO基本介绍
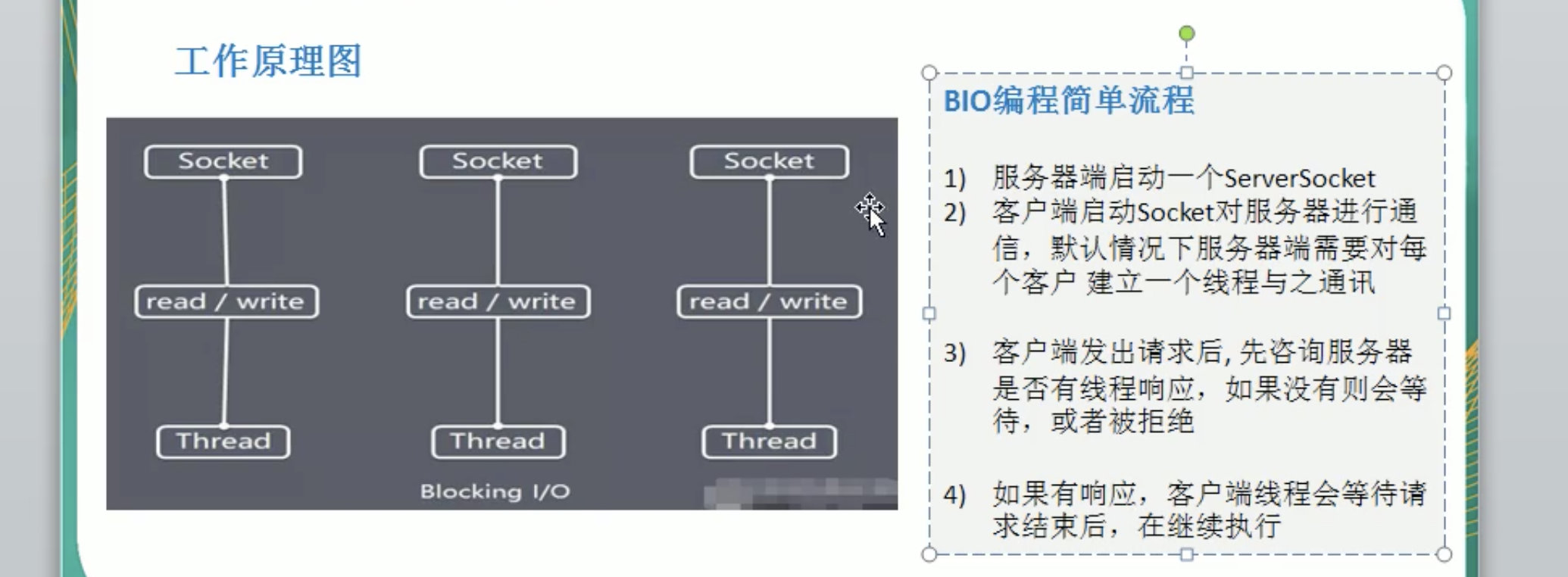
Java BIO 工作机制
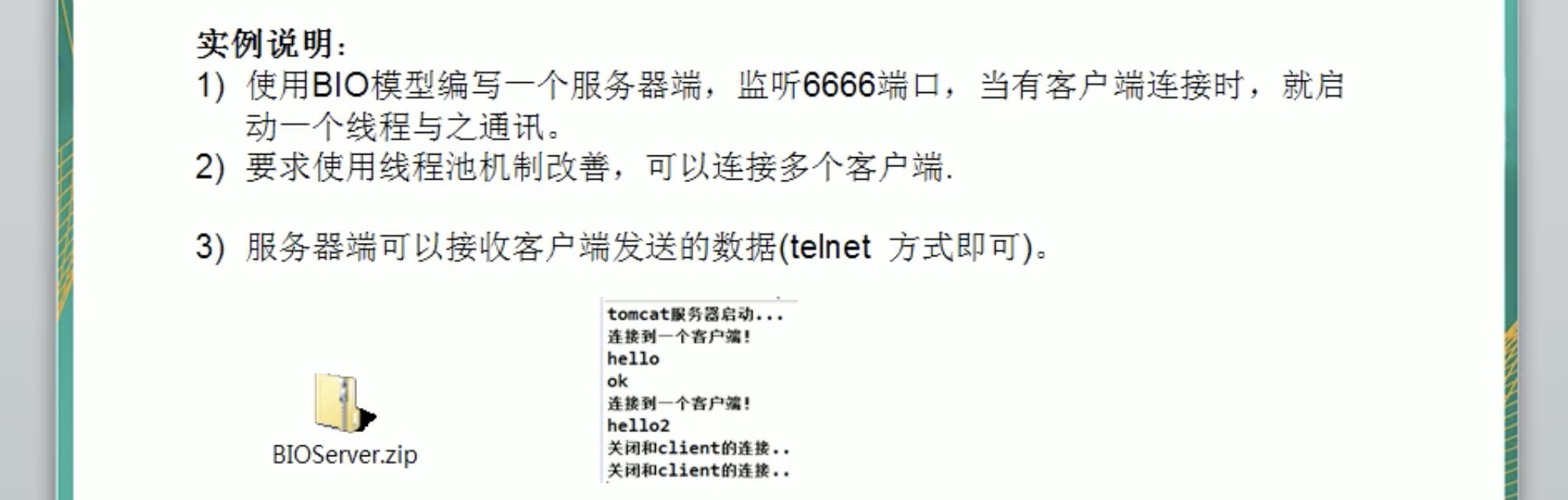
Java BIO 应用案例
// 代码示例:
public class BIOService {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 功能需求:
// 使用BIO模型编写一个服务器,监听6666窗口,当有客户端连接时,就启动一个客户端线程与之通信.
// 要求使用线程连接机制,可以连接多个客户端.
// 服务器端可以接受客户端发送的数据(telnet方式即可)
//1. 首先建立一个线程池.
ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
//2. 建立一个监听服务,来监听客户端连接
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(6666);
System.out.println("服务器启动成功");
while (true) {
// 监听,等待客户端连接
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("客户端连接了.");
//连接了之后,给这个用户创建一个线程用于通信.
newCachedThreadPool.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
//从写run方法. 接受客户端发送的消息.打印到控制台.
handler(socket);
}
});
}
}
private static void handler(Socket socket) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
try (InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream()) {
while (true) { //通过socket获取到输入流
int read = inputStream.read(bytes);
if (read != -1) { // 如果在读的过程中,打印出字节.
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
} else {//读完之后,退出循环
break;
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 我试试会报错不会.不关闭流,但是实用的try- which - resource
System.out.println("关闭连接");
}
}
}
Java BIO问题分析

Java NIO编程
JavaNIO基本介绍

NIO中的Channel 相当于 BIO当中的serverSocket。 非阻塞 是通过Buffer实现的。

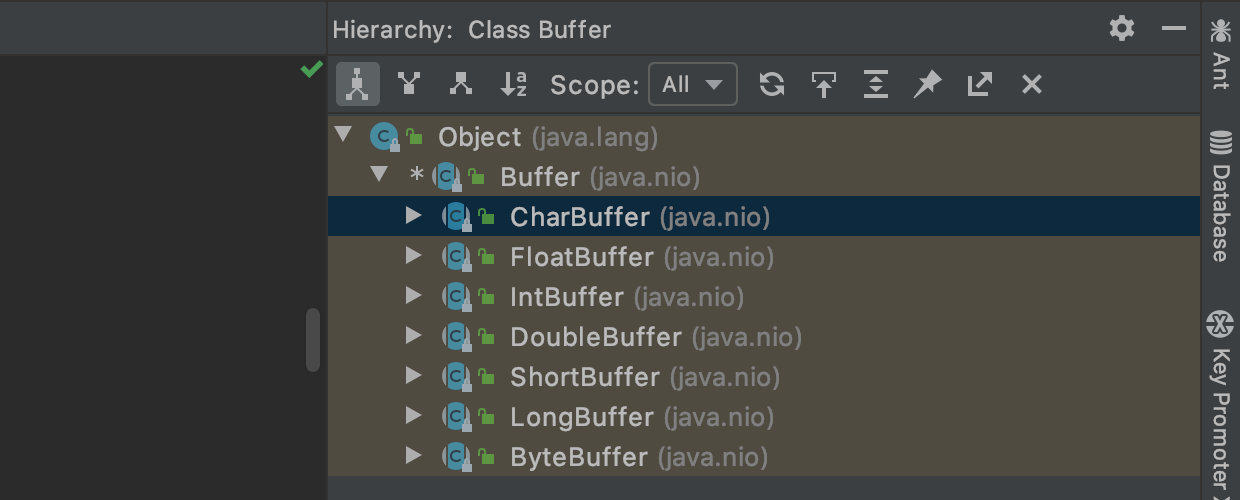
NIO Buffer的基本使用 案例介绍:
public class BasicBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
IntBuffer intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(5);
intBuffer.put(1);
intBuffer.put(2);
intBuffer.put(3);
intBuffer.put(4);
intBuffer.put(5);
intBuffer.flip(); // 转换读写操作.
while (intBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
int i = intBuffer.get();
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
NIO和BIO的比较

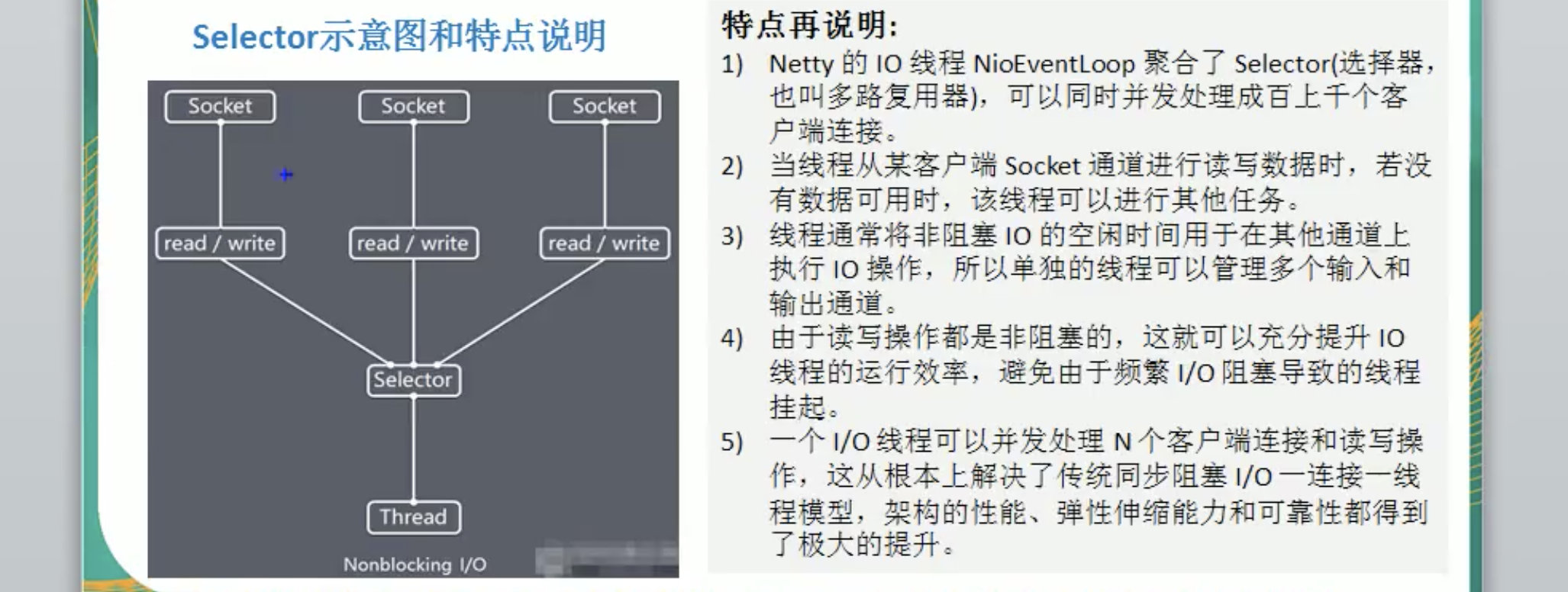
NIO三大核心原理示意图
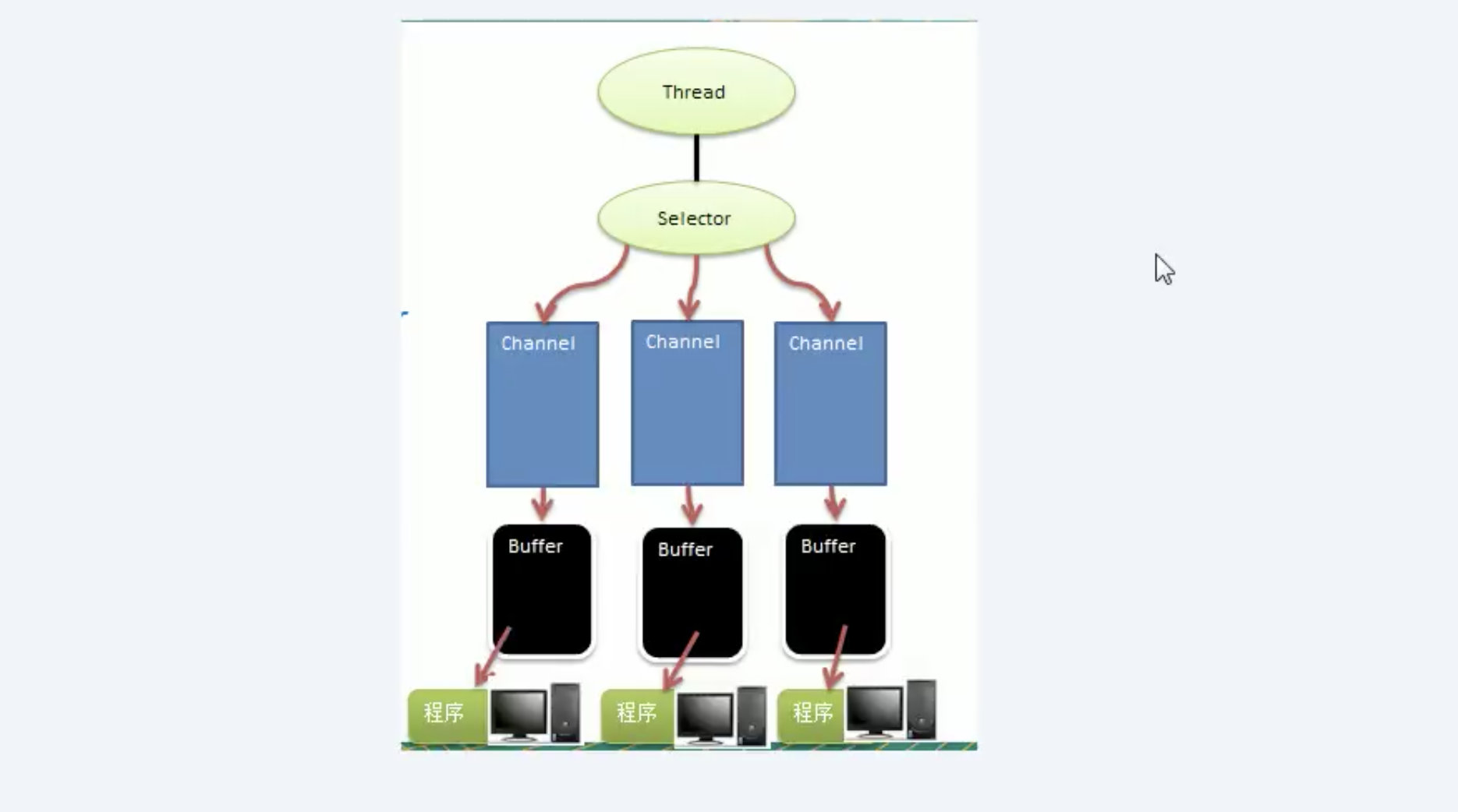
Selector 、 Channel 和Buffer的关系图的说明
- 每个channel都会对应一个Buffer
- Selector会对应一个线程。一个线程对应多个channel(连接)
- 该图反应了有三个channel注册到了该selector。
- 程序切换到哪个channel,是由事件决定的。Event是一个重要的概念。(后续会学习都有哪些事件)
- selector会根据不同的事件,在各个通道上切换。
- Buffer就是一个内存块,底层是有一个数组
- 数据的读取写入是通过Buffer,这个和BIO是有本质不同的。BIO中对于一个流而言,要么是输入流或者是输出流,不会是双向流动的。但是NIO的BUffer是可以读,也可以写的。但是需要使用flip()切换。
- Channel也是双向的。可以反应底层操作系统的情况。比如说Linux,底层的操作系统通到就是双向的。
NIO三大核心之—Buffer
Buffer基本介绍
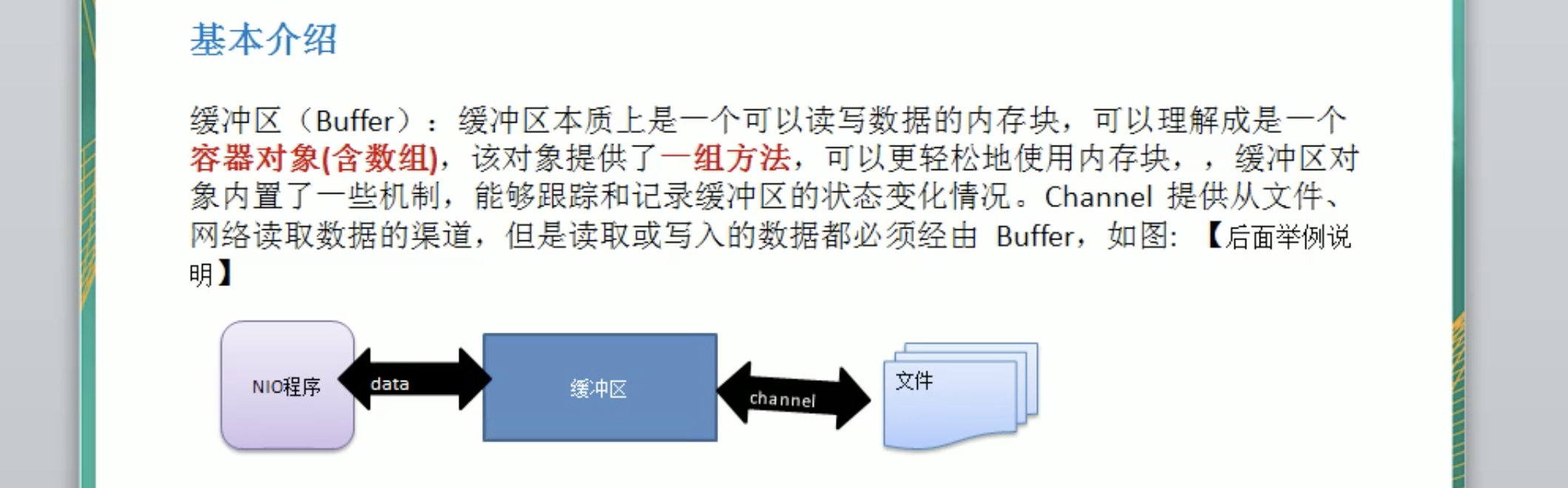
Buffer类及其子类 API

Buffer API

ByteBuffer API

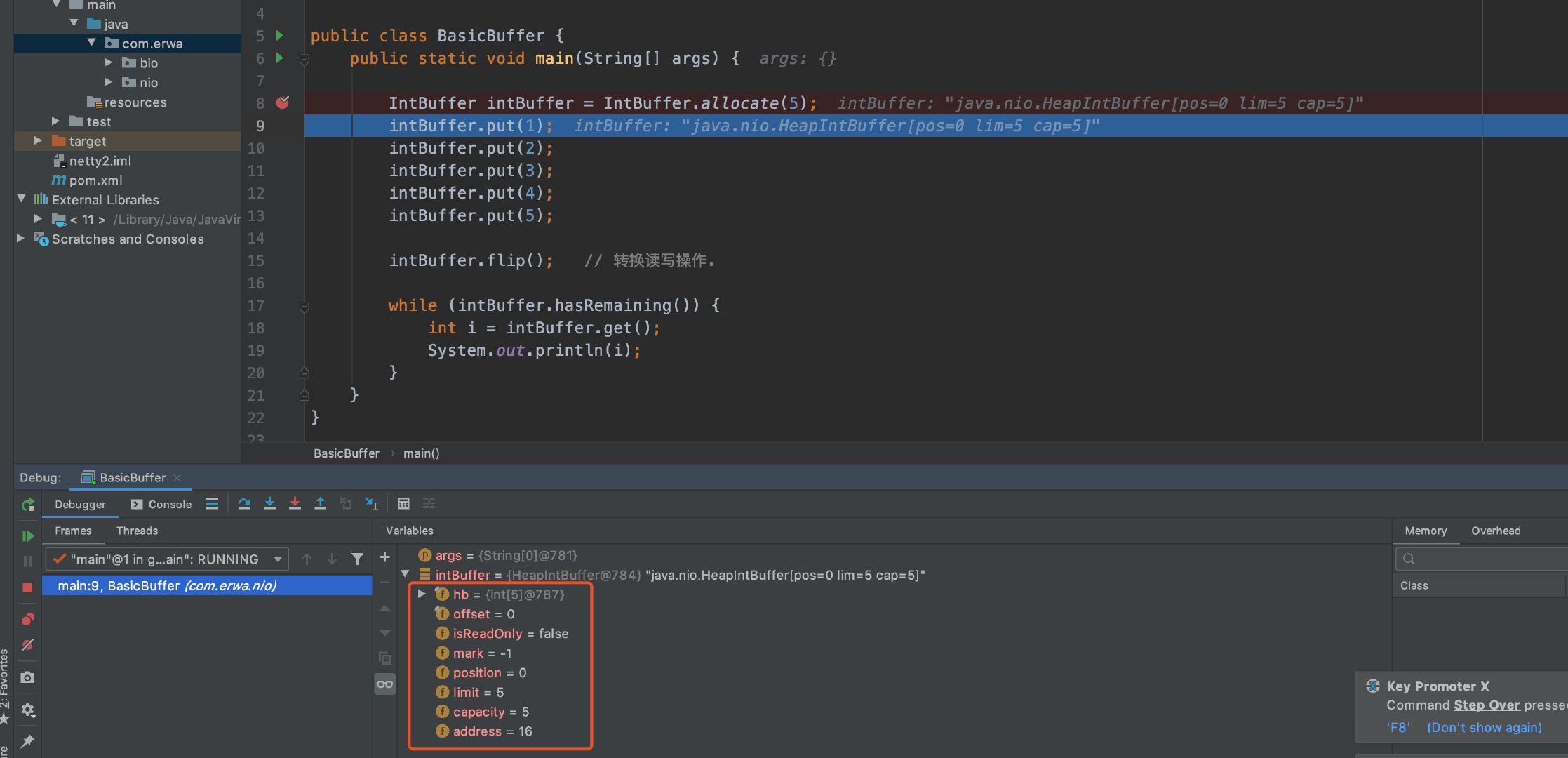
NIO三大核心之—Channel
基本介绍


ServerSocketChannel 类似ServerSocket
ServerChannel类似Server
举例:FileChannel类


实现流程示意图:
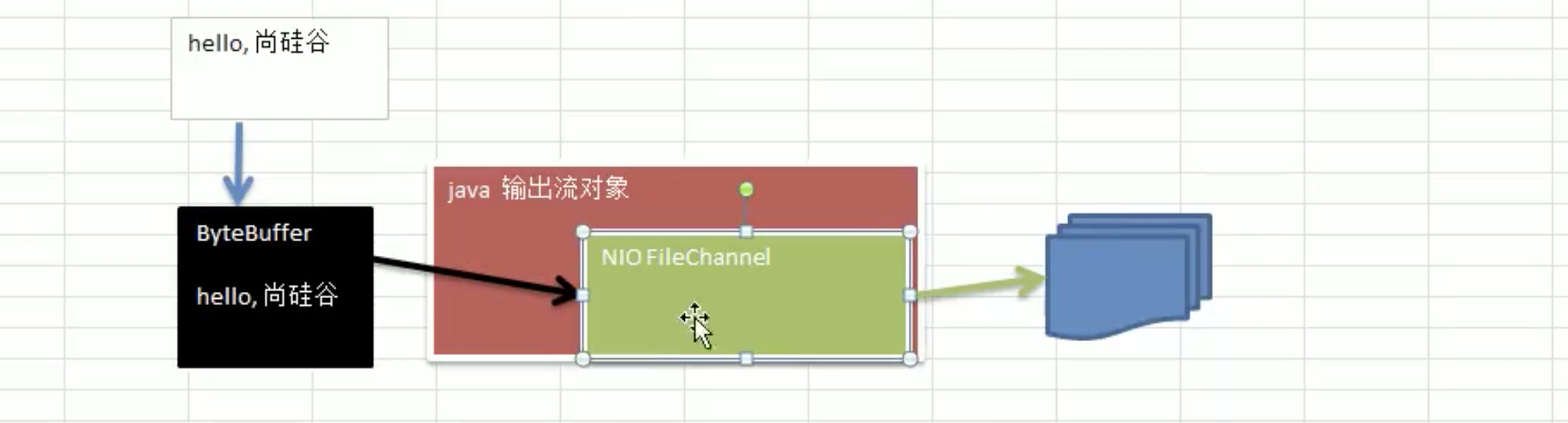
1. 应用实例: 本地文件写数据。 代码实现:
public class NIOFileBuffer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//将"hello,二娃"写入到hello.txt文件中
String str = "hello,二娃";
// 首先要创建一个输出流:
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("hello.txt");
//创建一个fileChannel通道
FileChannel fileOutputStreamChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
//创建一个ByteBuffer,将字符串写入到Buffer中
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
byteBuffer.put(str.getBytes());
//要对byteBuffer进行一个翻转
byteBuffer.flip();
//将byteBuffer写入到fileChannel中
fileOutputStreamChannel.write(byteBuffer);
//关闭流
fileOutputStream.close();
}
}
2. 本地文件读数据:
//创建一个输入流,读取文件内容
File file = new File("hello.txt");
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
//获取到输入流通到
FileChannel fileInputStreamChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
//准备一个byteBuffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate((int) file.length());
//将管道中的数据放入到byteBuffer中
fileInputStreamChannel.read(byteBuffer);
//输出内容
System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
fileInputStream.close();

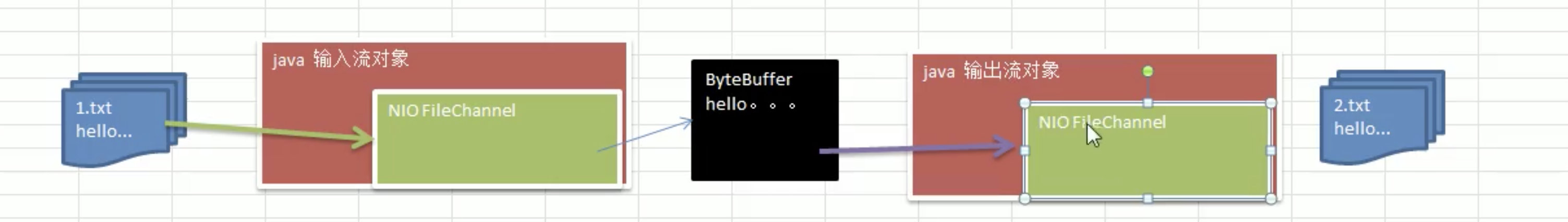
3. 使用一个Buffer完成文件的读取。 把文件A中的内容读取到,写入到文件B中。 示意图如上.代码如下:
//用一个Buffer完成文件的读写
try (
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("hello.txt"));
FileChannel fileInputStreamChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("hello2.txt"));
FileChannel fileOutputStreamChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
while (true) {
byteBuffer.clear();
int read = fileInputStreamChannel.read(byteBuffer);
if (read == -1) {
break;
}
byteBuffer.flip();
fileOutputStreamChannel.write(byteBuffer);
}
}
4. 拷贝文件。使用transferFrom方法
try(
// 使用拷贝方法,拷贝一个图片
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File("hello.txt"));
FileChannel fileInputStreamChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File("hello2.txt"));
FileChannel fileOutputStreamChannel = fileOutputStream.getChannel();
){
fileOutputStreamChannel.transferFrom(fileInputStreamChannel,0,fileInputStreamChannel.size());
}
关于Buffer和Channel的注意事项和细节

注意事项要注意。
1. Buffer支持类型化。 put的什么类型,读取的时候就要get相应的类型。 举例说明:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
byteBuffer.putInt(123);
byteBuffer.putChar('a');
byteBuffer.putLong(10L);
byteBuffer.putShort((short)234);
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.println(byteBuffer.getInt());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.getChar());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.getLong());
System.out.println(byteBuffer.getShort());
//顺序如果不同,可能会导致程序抛出异常。java.nio.BufferUnderflowException
}
2. 可以将一个普通Buffer转成只读Buffer。只读Buffer只能读。写操作时会抛 ReadOnlyBufferException
举例说明:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(32);
for (int i = 0; i < byteBuffer.capacity(); i++) {
byteBuffer.put((byte) i);
}
byteBuffer.flip();
ByteBuffer asReadOnlyBuffer = byteBuffer.asReadOnlyBuffer();
while (asReadOnlyBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
System.out.print(asReadOnlyBuffer.get()+ " ");
}
asReadOnlyBuffer.put((byte) 12); //已经转换成readBuffer。此时pur会抛异常ReadOnlyBufferException
}
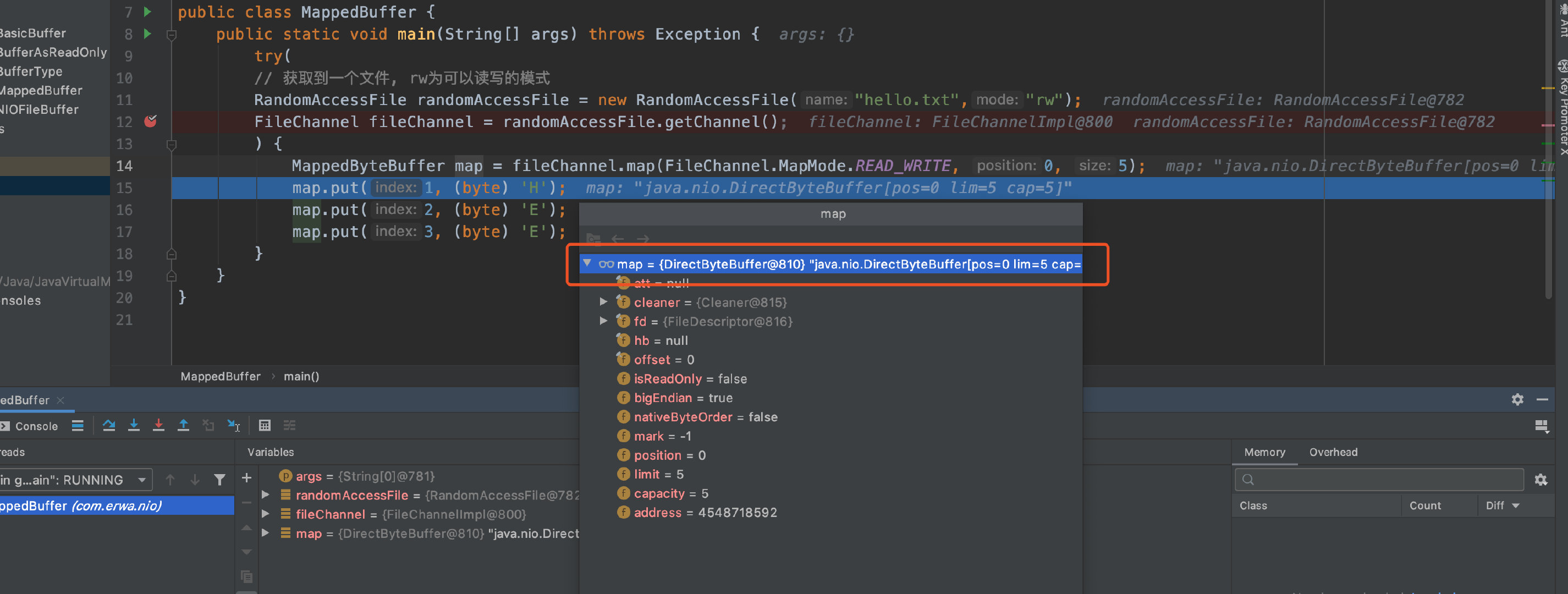
3. MappedByteBuffer
作用: 可让文件直接在内部(堆外内存)修改,操作系统不需要拷贝一次。
// 参数1. FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE 使用的读写模式
// 参数2 : 0 可以直接修改的起始位置
// 参数3 : 5 是映射到内存的大小(不是索引位置)。即将1.txt的多少个字节映射到内存
//可以直接修改的范围就是0-5
// MappedByteBuffer 的实际类型是 DirectByteBuffer
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
try(
// 获取到一个文件, rw为可以读写的模式
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile("hello.txt","rw");
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
) {
MappedByteBuffer map = fileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 5);
map.put(1, (byte) 'H');
map.put(2, (byte) 'E');
map.put(3, (byte) 'E');
}
}
4. Scattering 和 Gathering ; 分散和聚合。
之前我们都是使用一个Buffer来操作的。NIO还支持多个Buffer(即Buffer数组)来完成读写操作。即 分散和聚合。
//Scattering 将数据写入到Buffer时,可以采用Buffer数组,依次写入。[分散]
//Gathering 从Buffer读取数据时,可以采用Buffer数组,依次读【聚合】
//这次使用 ServerSocketChannel 和 SocketChannel 网络 来操作。
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress(7000);
// 绑定端口到socket ,并启动
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(inetSocketAddress);
// 创建一个Buffer数组
ByteBuffer[] byteBuffers = new ByteBuffer[2];
byteBuffers[0] = ByteBuffer.allocate(5);
byteBuffers[1] = ByteBuffer.allocate(3);
//等待客户端连接(使用telnet)
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("连接成功");
long messageLength = 8;
//连接成功,循环读取
while (true) {
int byteRead = 0;
while (byteRead < messageLength) {
long l = socketChannel.read(byteBuffers);
byteRead += l;
System.out.println("当前的byteRead: " + byteRead);
//使用流打印,打印出当前的Buffer中的 limit , position
Arrays.stream(byteBuffers).map(byteBuffer -> "position" + byteBuffer.position() + ", limit "
+ byteBuffer.limit()).forEach(System.out::println);
}
//将所有的Buffer进行flip
Arrays.stream(byteBuffers).map(ByteBuffer::flip);
//将数据读出返回给客户端
long byteWrite = 0;
while (byteWrite < messageLength) {
long write = socketChannel.write(byteBuffers);
byteWrite += write;
}
//将所有的BUffer进行clean
Arrays.stream(byteBuffers).map(ByteBuffer::clear);
System.out.println("readLength " + byteRead + "writeLength " + byteWrite);
}
}
NIO三大核心之—Selector
Selector基本介绍

selector API
selector类中实现的方法及其方法功能的说明。列出来功能,更能方便的使用。
重点记着- open方法,返回一个selector。


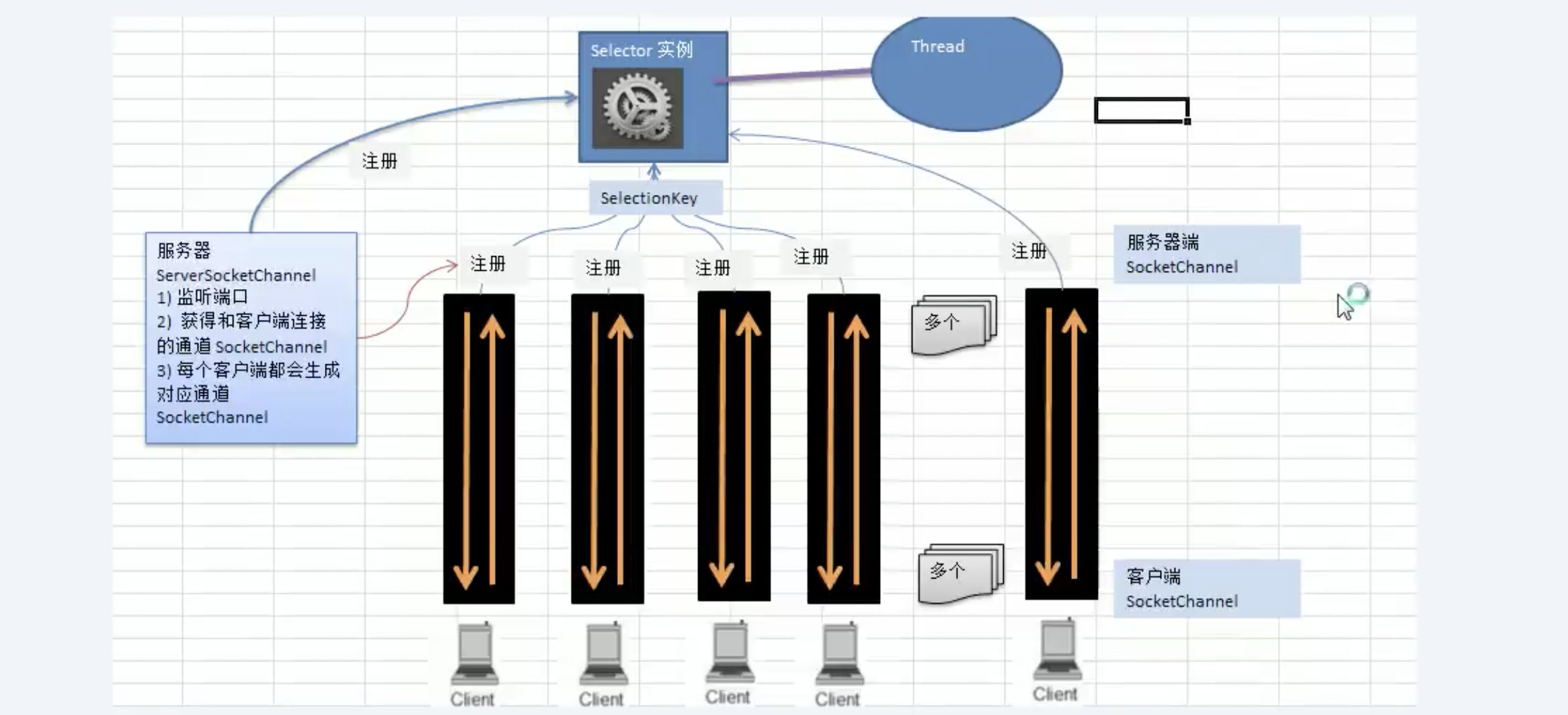
NIO 非阻塞网络编程原理分析图
对下图的说明:
- 当客户端连接时,会通过serverSocketChannel得到一个对应的SocketChannel
- Selector进行监听(使用Select方法),返回有事件发生的通道的个数。
- 将socketChannel注册到selector上。一个selector上可以注册多个socketChannel。(SelectableChannel.register(Selectoe sel, int ops))。ops参数的说明:有4个状态。
- 注册后返回一个SelectionKey,会和该selector关联(集合的方式关联)。
- 进一步得到各个SelectionKey(有事件发生的的SelectionKey)
- 再通过SelectionKey反向获取注册的socketChannel。(使用SelectionKey.channel()方法)
- 可以得到channel,完成业务处理。

实例代码案例演示: NIO非阻塞网络编程通讯
服务器端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// NIO非阻塞网络编程通讯 -- 服务器端
// 1. 创建serverSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 2. 得到一个Selector对象
Selector selector = Selector.open();
// 3. 绑定一个端口6666, 在服务器端监听
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(6666));
// 4. 设置为非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 5. 把serverSocketChannel注册到Selector,关心事件op_accept
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 6. 循环等待客户端连接
while (true) {
// 等待一秒钟,如果没有客户端事件发生,不等待了。
if ((selector.select(1000) == 0)) {
//没有事件发生
System.out.println("服务器上一秒中,没有客户端连接");
continue;
}
// 如果返回的>0 ,就获取到相关的 selectionKeys集合。
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> selectionKeyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
// 通过selectionKeys反向获取通道,处理业务
while (selectionKeyIterator.hasNext()) {
// 获取selectionKey
SelectionKey selectionKey = selectionKeyIterator.next();
// 根据key对应的通道事件,做相应的处理
if (selectionKey.isAcceptable()) {
//给此客户端分配一个socketChannel
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
System.out.println("客户端连接了, " + selectionKey.hashCode());
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//将此channel注册到 selector上, 关注read事件
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ, ByteBuffer.allocate(1024));
}
if (selectionKey.isReadable()) { //发生了 read事件
//通过key,反向获取到对应的channel
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) selectionKey.channel();
//获取到该key的buffer
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = (ByteBuffer) selectionKey.attachment();
channel.read(byteBuffer);
System.out.println("from 客户端 : " + new String(byteBuffer.array()));
}
//手动移除key
selectionKeyIterator.remove();
}
}
}
客户端:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 1. 得到一个网络通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
// 2. 提供非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 3. 提供服务器端的IP和端口
InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress = new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666);
// 4. 连接服务器
if (!socketChannel.connect(inetSocketAddress)) {
// 连接不成功, 打印一句话,代表这时候不阻塞,可以去做别的事情
while (!socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
System.out.println("客户端连接未成功,先去干别的事情了");
}
}
// 5. 如果连接成功,发送数据。 通过ByteBuffer.wrap (根据字节的大小自动放入到Buffer中。)
String str = "hello,二娃";
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap(str.getBytes());
// 6. 发送数据。将Buffer数据写入channel。
socketChannel.write(byteBuffer);
System.in.read();
}
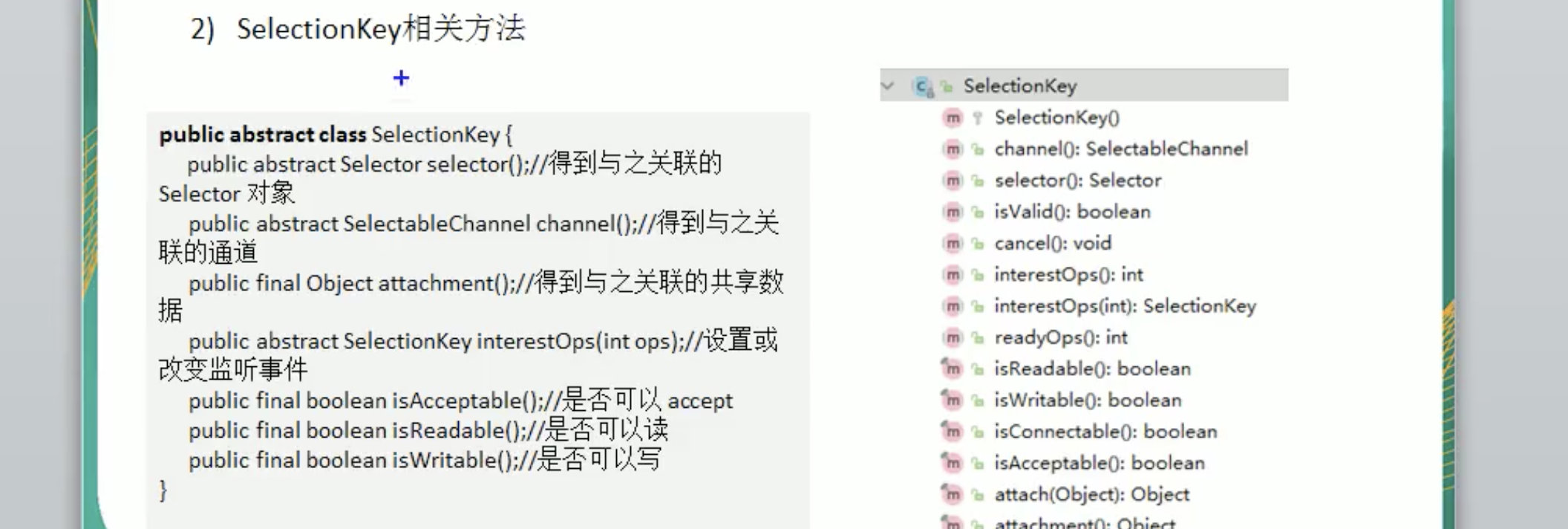
SelectionKey API
每注册一个客户端,会出现一个新的channel ,selectionkey.keys()就会增加1
selectionKeys.size() ; 活动的channel的个数。
selectionkeys.keys(); 总的channel的个数。

注意,这时候我看了一下源码, selector真正的实现方法已经和视频中老师的不一样了。
下图是老师视频中的 和 我自己的方法对比。 原因是 老师的电脑是Windows,我的是Mac
ServerSocketChannel API

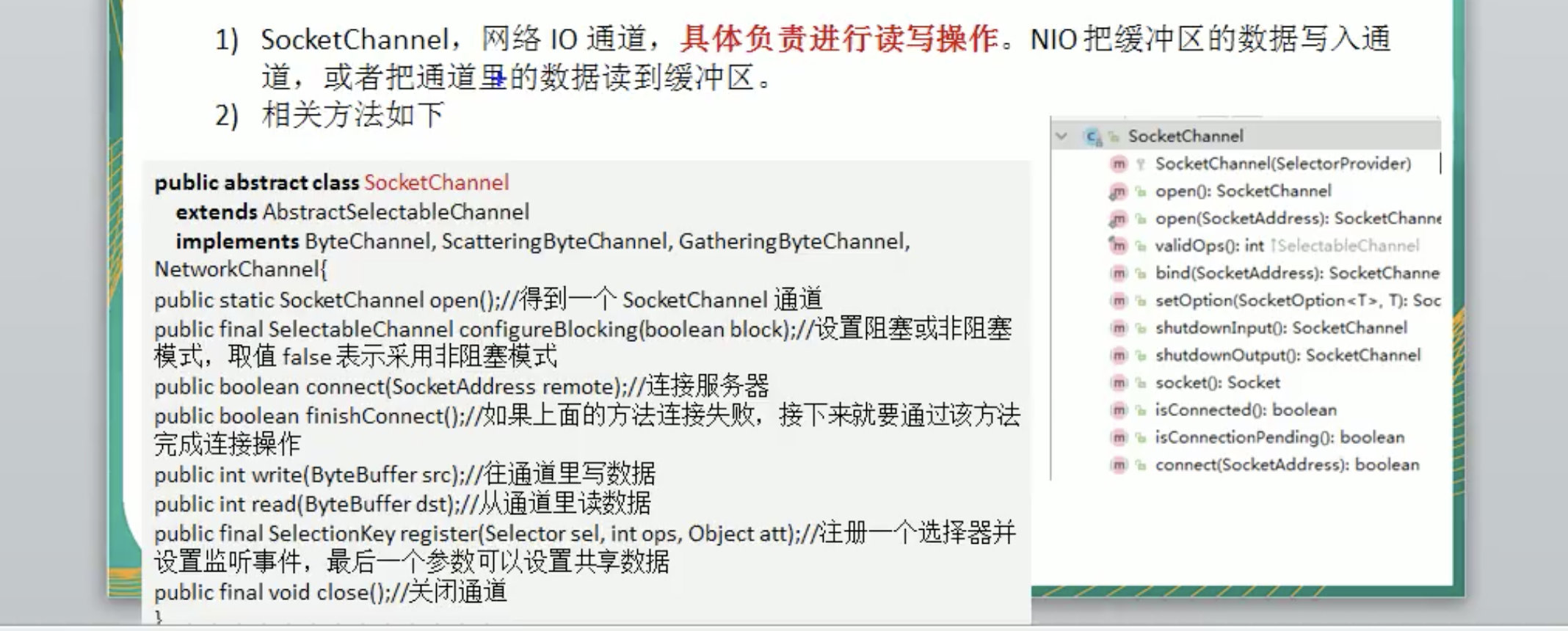
SocketChannel API
NIO网络编程应用实例-群聊系统
完成这个群聊系统的代码案例

开发流程:
1. 先编写服务器端
1.1 服务器启动并监听6667
1.2 服务器接受客户端信息,并实现转发【处理上线和离线】
2.编写客户端
2.1 连接服务器
2.2 发送消息
2.3 接受服务器的消息
1.初始化构造器,
2. 监听
服务器端代码:
/**
* weChat服务器端
* 1. 先编写服务器端
* 1.1 服务器启动并监听6667
* 1.2 服务器接受客户端信息,并实现转发【处理上线和离线】
*/
public class weCharServer {
private ServerSocketChannel listenSocketChannel ;
private Selector selector;
private static final int PORT = 6666;
public weCharServer() throws IOException {
//1. 得到选择器
selector = Selector.open();
//2. 得到 serverSocketChannel
listenSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//3. 绑定端口
listenSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(PORT));
//4. 设置非阻塞
listenSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//5. 注册
listenSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
}
/**
* 监听
*/
public void listen(){
try {
while (true) {
int count = selector.select(2000);
if (count > 0) {
//有事件处理
//遍历得到selectionKeys集合
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
//取出selectionKey
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
//监听到accept
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
SocketChannel sc = listenSocketChannel.accept();
//将 该 SocketChannel注册到 selector 上
sc.configureBlocking(false);
sc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//提示上线
System.out.println(sc.getRemoteAddress() + "上线了");
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
//通道发送read事件,即通道是刻度的状态
keyRead(key);
}
iterator.remove();
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void keyRead(SelectionKey key) {
SocketChannel channel = null;
try {
//根据key得到channel
channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//创建Buffer
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int read = channel.read(buffer);
//根据read只,做处理
if (read > 0) {
//把缓存区的数据转成字符串
String msg = new String(buffer.array());
System.out.println("from 客户端 : " + msg);
//向其他客户转发消息
sendInfoToOtherClient(msg,channel);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
System.out.println(channel.getRemoteAddress() + " 离线了");
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void sendInfoToOtherClient(String msg, SocketChannel self) throws IOException {
System.out.println("服务器转发消息中...");
//遍历所有注册到selector上的socketChannel,并排除self
for (SelectionKey key : selector.keys()) {
//通过key取出对应的socketChannel
SelectableChannel targetChannel = key.channel();
//排除自己
if (targetChannel instanceof SocketChannel && targetChannel != self) {
//将Buffer中的数据写入通道
((SocketChannel) targetChannel).write(ByteBuffer.wrap(msg.getBytes()));
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
weCharServer weCharServer = new weCharServer();
weCharServer.listen();
}
}
客户端代码:
public class weChatClient {
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private String username;
private Selector selector;
public weChatClient() throws IOException {
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 6666));
//设置为非阻塞
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//注册
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
username = socketChannel.getLocalAddress().toString().substring(1);
System.out.println("username : " + username);
}
//向服务器发送消息
public void senInfo(String info) {
info = username + " 说 : " + info;
try {
socketChannel.write(ByteBuffer.wrap(info.getBytes()));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//从服务器读取消息
public void readInfo(){
try {
int readChannels = selector.select();
if (readChannels > 0) {
//有可用的通道
Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = iterator.next();
if (key.isReadable()) { //读事件
//得到相关的通道
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//得到一个缓冲区
ByteBuffer allocate = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
sc.read(allocate);
//把读取的数据转换成字符换
String msg = new String(allocate.array());
System.out.println(msg.trim());
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//启动一个客户端
weChatClient chatClient = new weChatClient();
//启动一个线程,每三秒读取从服务器发送的数据
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
chatClient.readInfo();
try {
Thread.currentThread().sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
//发送消息给服务器端
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
chatClient.senInfo(scanner.nextLine());
}
}
}
NIO与零拷贝
零拷贝,是指从操作系统看的,不经过CPU拷贝。
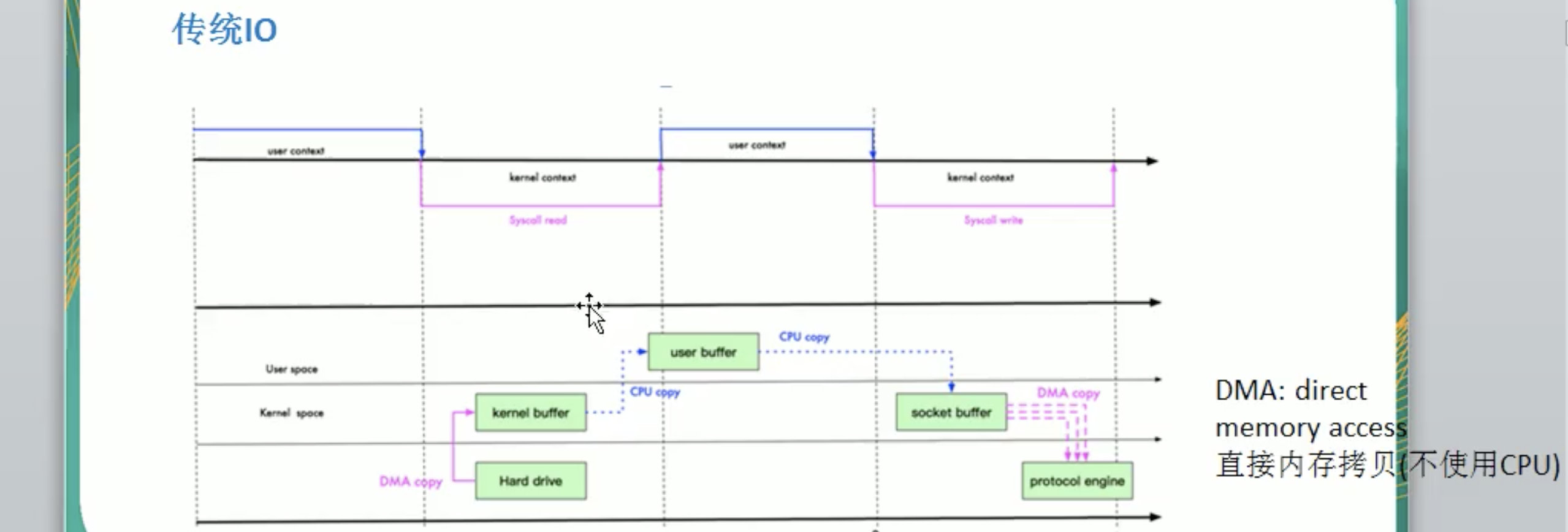
什么是DMA(direct memory access)? 直接内存拷贝(不适用CPU)。

传统IO数据读写

什么是DMA(direct memory access)? 直接内存拷贝(不适用CPU)
传统的IO:使用了4次拷贝,3次状态的转换。
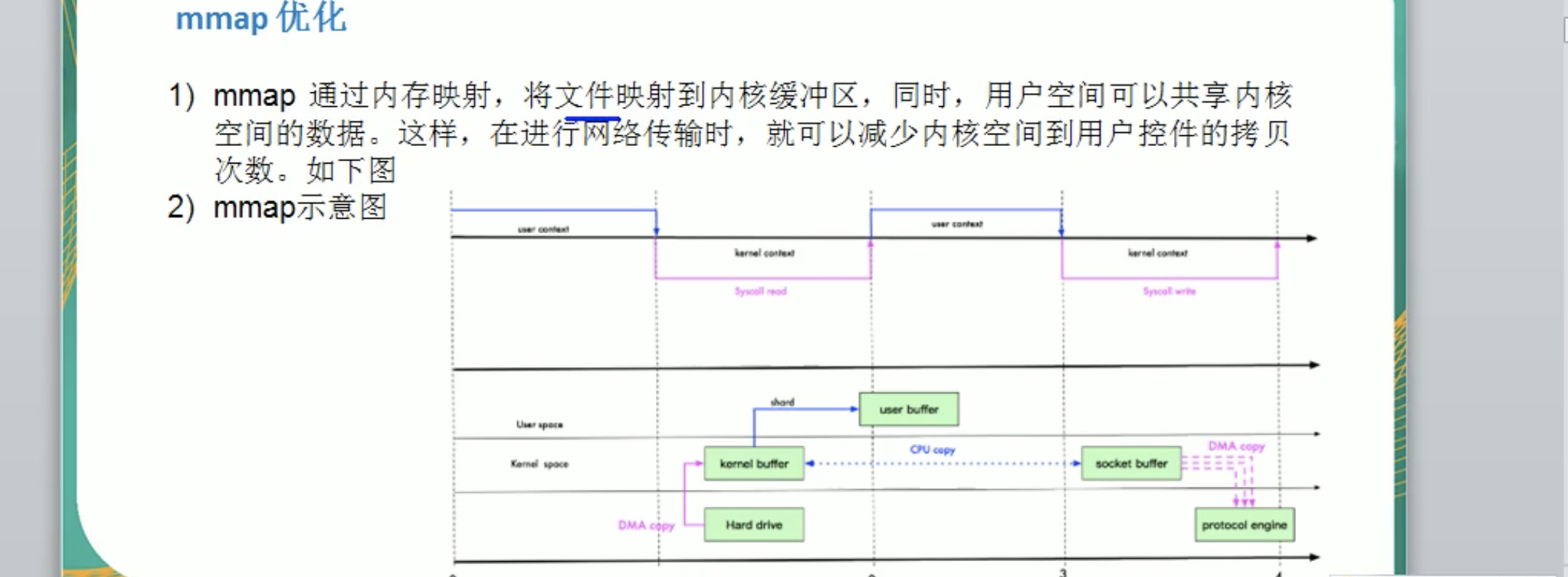
mmap优化
mmap优化:使用了3次拷贝,3次状态切换。
sendFile优化
sendFile 优化: 使用3次拷贝,2次状态切换。
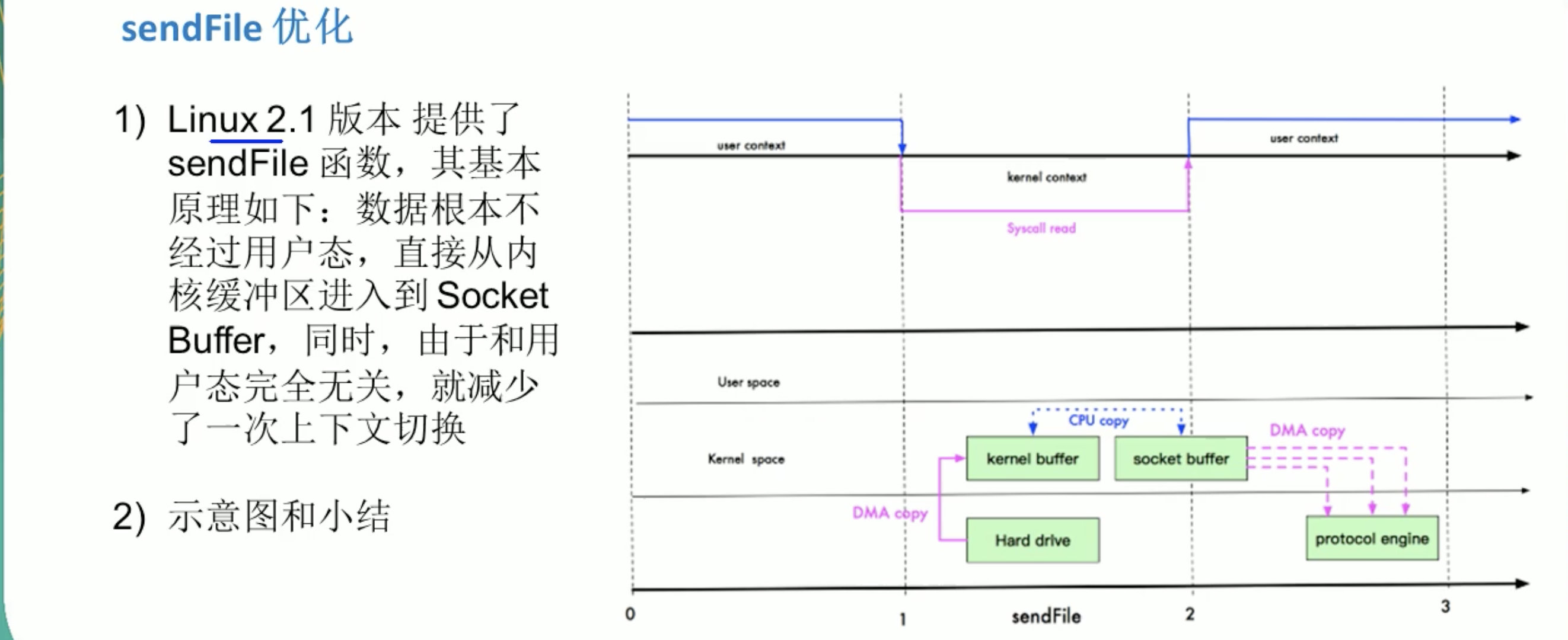
sendFile 进一步优化: 使用2次拷贝,2次上下文状态切换。
这里还是有一次CPU拷贝的。 从kernel buffer -> socket buffer . 但是拷贝的信息很少。比如 length ,offet ,消耗低,可以忽略。
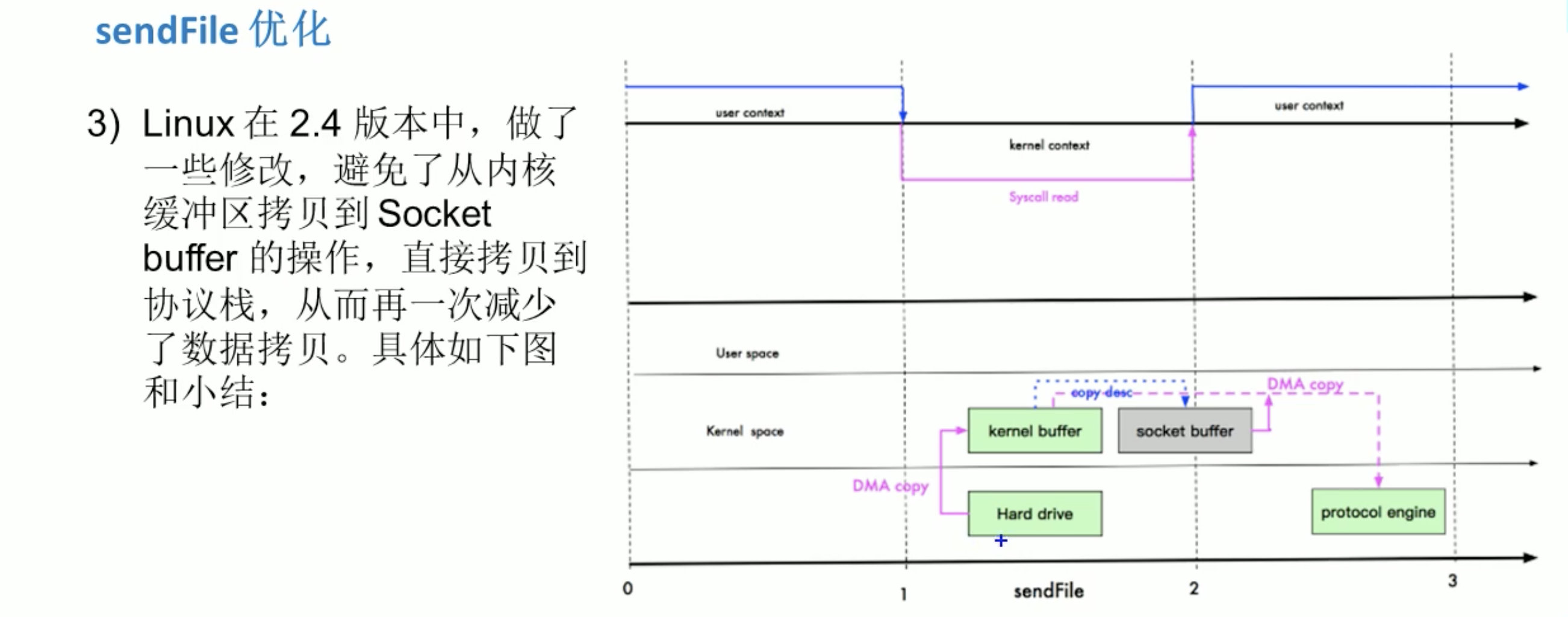

mmap 和 sendFile的区别

NIO零拷贝案例

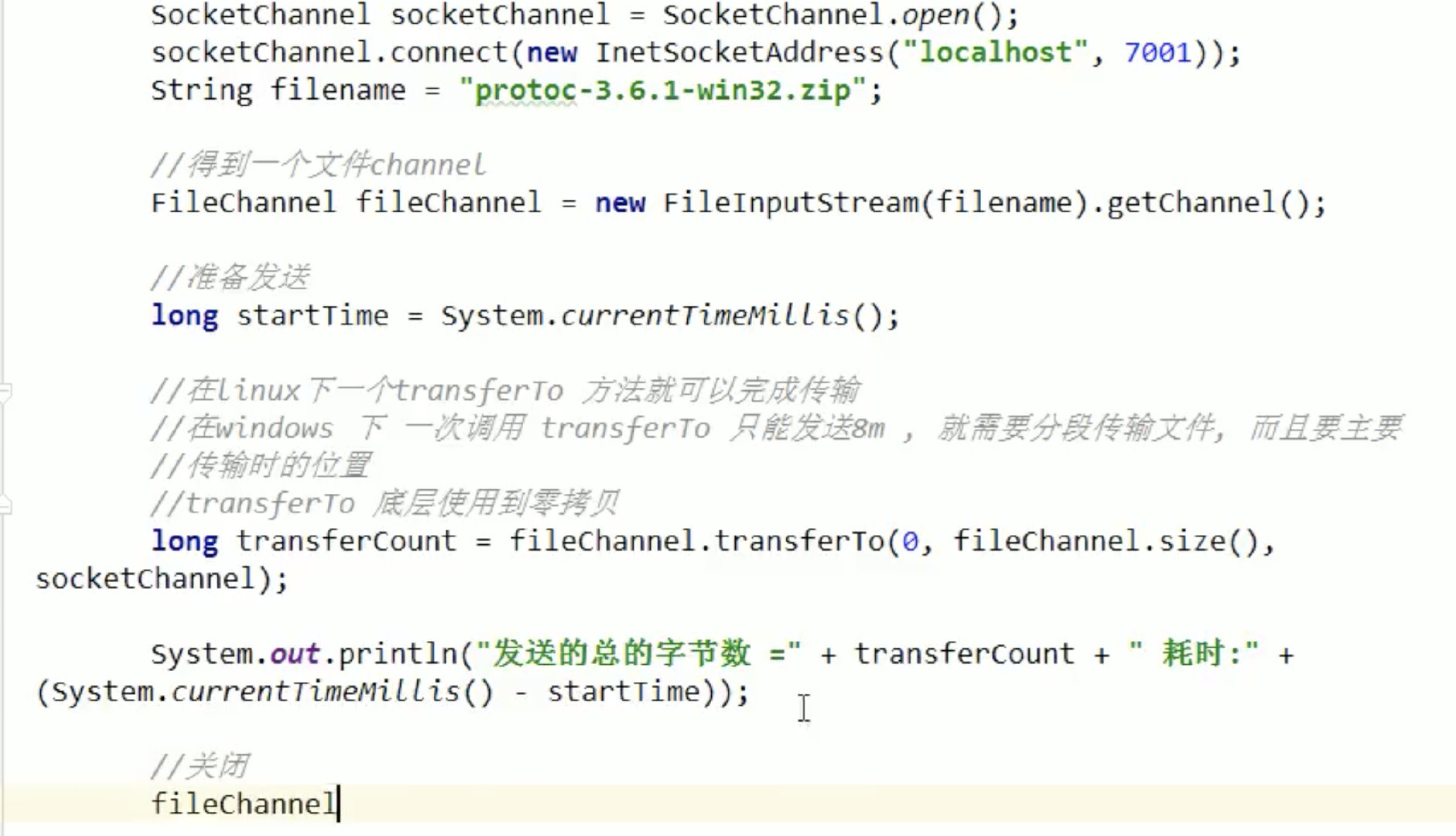
transferTo注意事项 :
1. 在Linux下,一个transferTo方法就可以传输完、
2. 在Windows下一次调用transferTo只能传输8M,而且要注意传输时的位置。
使用方法:
fileChannel.transferTo(0,fileChannel.size(),socketChannel); 从0开始传,传多少个。
Java AIO编程

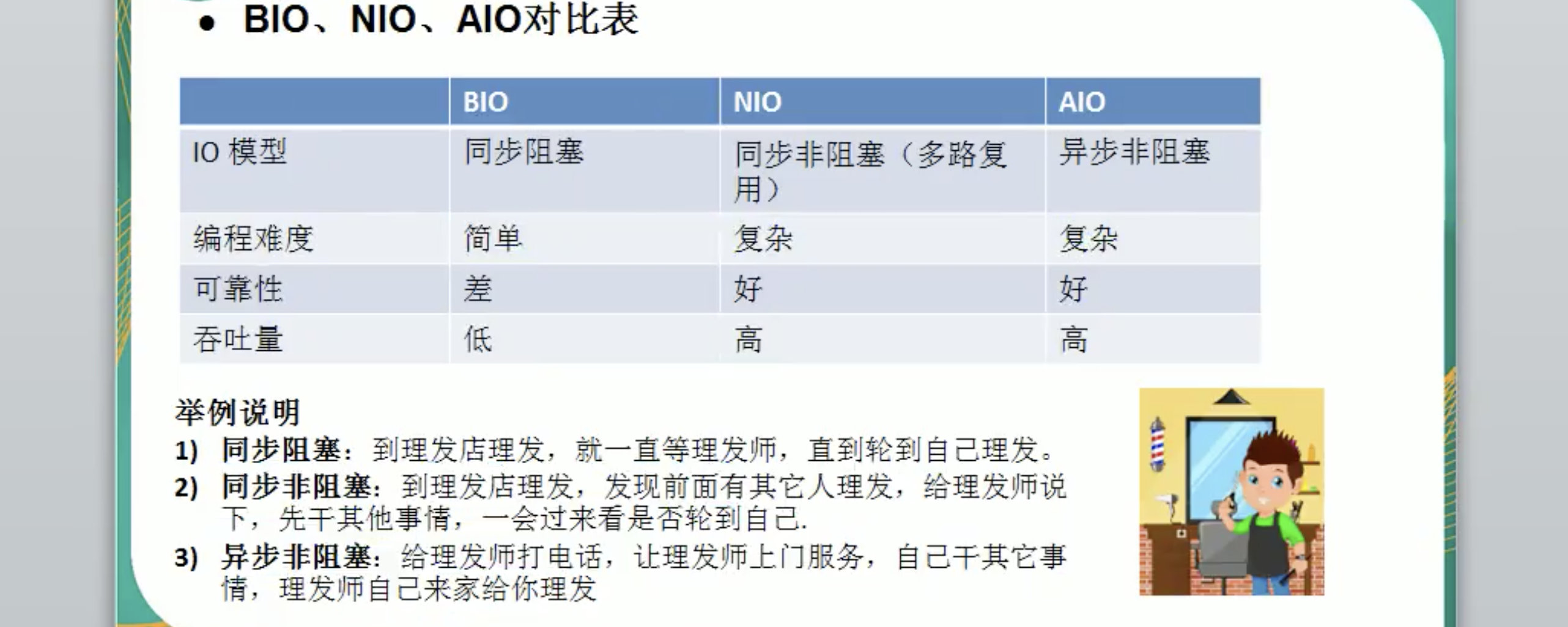
BIO、NIO、AIO对比