传统的js是使用函数和原型链的方式用来模拟类
es6中加入了类,class关键字
类
// 定义类
class Greeter {
greeting: string;
constructor(message: string){
this.greeting = message; // 使用this表示访问的是类成员
}
greet() {
return "Hello," + this.greeting;
}
}
// 创建对象
let greeter = new Greeter("World");编译后的js文件如下
es5
// 定义类
var Greeter = /** @class */ (function () {
function Greeter(message) {
this.greeting = message;
}
Greeter.prototype.greet = function () {
return "Hello," + this.greeting;
};
return Greeter;
}());
// 创建对象
var greeter = new Greeter("World");
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.mapes6
// 定义类
class Greeter {
constructor(message) {
this.greeting = message;
}
greet() {
return "Hello," + this.greeting;
}
}
// 创建对象
let greeter = new Greeter("World");
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map继承
在ts中可以使用类似于Java中的类的继承。
// 定义类
class Animal {
move(distanceInMeters: number = 0) { // 定义一个方法
console.log("class - Animal move 方法" + distanceInMeters);
}
}
// 定义继承类
class Dog extends Animal {
bark() {
console.log("Dog!");
}
}
const dog = new Dog(); // 创建给予Dog类的对象
dog.bark(); // 调用继承类的方法bark()
dog.move(10); // 调用父类的move方法
dog.bark();var __extends = (this && this.__extends) || (function () {
var extendStatics = function (d, b) {
extendStatics = Object.setPrototypeOf ||
({ __proto__: [] } instanceof Array && function (d, b) { d.__proto__ = b; }) ||
function (d, b) { for (var p in b) if (b.hasOwnProperty(p)) d[p] = b[p]; };
return extendStatics(d, b);
}
return function (d, b) {
extendStatics(d, b);
function __() { this.constructor = d; }
d.prototype = b === null ? Object.create(b) : (__.prototype = b.prototype, new __());
};
})();
// 定义类
var Animal = /** @class */ (function () {
function Animal() {
}
Animal.prototype.move = function (distanceInMeters) {
if (distanceInMeters === void 0) { distanceInMeters = 0; }
console.log("class - Animal move 方法" + distanceInMeters);
};
return Animal;
}());
// 定义继承类
var Dog = /** @class */ (function (_super) {
__extends(Dog, _super);
function Dog() {
return _super !== null && _super.apply(this, arguments) || this;
}
Dog.prototype.bark = function () {
console.log("Dog!");
};
return Dog;
}(Animal));
var dog = new Dog(); // 创建给予Dog类的对象
dog.bark(); // 调用继承类的方法bark()
dog.move(10); // 调用父类的move方法
dog.bark();
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map超类
class Animal {
name: string;
constructor(theName: string){
this.name = theName;
}
move(distanceInMeters: number = 0){
console.log("distanceInMeters " + distanceInMeters);
}
}
class Snake extends Animal {
constructor(name: string){
super(name); // 调用父类的构造方法,在构造函数访问this之前,必须调用一次 super()
};
move(distanceInMeters = 45){ // 重写父类的move方法
console.log("Galloping...");
super.move(distanceInMeters); // 调用父类的move方法
}
};
class Horse extends Animal {
constructor(name: string){
super(name); // 调用父类的构造方法
}
move(distanceInMeters = 45){ // 重写move方法
console.log("Galloping...");
super.move(distanceInMeters); // 调用父类的move
}
}
// 调用基类的派生类即Snake类,使用的是基类的构造方法,重写了基类的move方法,并在子类的move方法中调用了父类的move方法
let sam = new Snake("Sammy the Python");
let tom: Animal; // 声明tom对象,其为Animal类
tom = new Horse("Tommy the Palomino"); // 此处赋值为Horse类,重写了Animal中的move方法
sam.move();
tom.move();var __extends = (this && this.__extends) || (function () {
var extendStatics = function (d, b) {
extendStatics = Object.setPrototypeOf ||
({ __proto__: [] } instanceof Array && function (d, b) { d.__proto__ = b; }) ||
function (d, b) { for (var p in b) if (b.hasOwnProperty(p)) d[p] = b[p]; };
return extendStatics(d, b);
}
return function (d, b) {
extendStatics(d, b);
function __() { this.constructor = d; }
d.prototype = b === null ? Object.create(b) : (__.prototype = b.prototype, new __());
};
})();
var Animal = /** @class */ (function () {
function Animal(theName) {
this.name = theName;
}
Animal.prototype.move = function (distanceInMeters) {
if (distanceInMeters === void 0) { distanceInMeters = 0; }
console.log("distanceInMeters " + distanceInMeters);
};
return Animal;
}());
var Snake = /** @class */ (function (_super) {
__extends(Snake, _super);
function Snake(name) {
return _super.call(this, name) || this;
}
;
Snake.prototype.move = function (distanceInMeters) {
if (distanceInMeters === void 0) { distanceInMeters = 45; }
console.log("Galloping...");
_super.prototype.move.call(this, distanceInMeters); // 调用父类的move方法
};
return Snake;
}(Animal));
;
var Horse = /** @class */ (function (_super) {
__extends(Horse, _super);
function Horse(name) {
return _super.call(this, name) || this;
}
Horse.prototype.move = function (distanceInMeters) {
if (distanceInMeters === void 0) { distanceInMeters = 45; }
console.log("Galloping...");
_super.prototype.move.call(this, distanceInMeters); // 调用父类的move
};
return Horse;
}(Animal));
// 调用基类的派生类即Snake类,使用的是基类的构造方法,重写了基类的move方法,并在子类的move方法中调用了父类的move方法
var sam = new Snake("Sammy the Python");
var tom; // 声明tom对象,其为Animal类
tom = new Horse("Tommy the Palomino"); // 此处赋值为Horse类,重写了Animal中的move方法
sam.move();
tom.move();
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map公有私有,保护修饰符
public 默认
public为默认
class Animal {
public name: string;
public constructor(theName: string){
this.name = theName;
}
public move(distanceInMeters: number){
console.log("move 方法");
}
}
var Animal = /** @class */ (function () {
function Animal(theName) {
this.name = theName;
}
Animal.prototype.move = function (distanceInMeters) {
console.log("move 方法");
};
return Animal;
}());
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.mapprivate 保护成员
不能被外部访问
class Person {
protected name: string; // 保护成员,对外不可访问
constructor(name:string){
this.name = name;
}
}
class Employee extends Person {
private department: string;
constructor(name:string, department:string){
super(name); // 调用父类的构造方法
// 接着才能使用this
this.department = department;
}
public getElevatorPitch(){
return "hello !" + name; // 通过实例访问父类的name
}
}
let howard = new Employee("Howard", "sales");
console.log(howard.getElevatorPitch());
//console.log(howard.name); //访问父类的,失败,不能直接被访问,但是能被派生方法所访问PS C:\Users\mingm\Desktop\ts> tsc
Active code page: 65001
PS C:\Users\mingm\Desktop\ts>var __extends = (this && this.__extends) || (function () {
var extendStatics = function (d, b) {
extendStatics = Object.setPrototypeOf ||
({ __proto__: [] } instanceof Array && function (d, b) { d.__proto__ = b; }) ||
function (d, b) { for (var p in b) if (b.hasOwnProperty(p)) d[p] = b[p]; };
return extendStatics(d, b);
}
return function (d, b) {
extendStatics(d, b);
function __() { this.constructor = d; }
d.prototype = b === null ? Object.create(b) : (__.prototype = b.prototype, new __());
};
})();
var Person = /** @class */ (function () {
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
return Person;
}());
var Employee = /** @class */ (function (_super) {
__extends(Employee, _super);
function Employee(name, department) {
var _this = _super.call(this, name) || this;
// 接着才能使用this
_this.department = department;
return _this;
}
Employee.prototype.getElevatorPitch = function () {
return "hello !" + name; // 通过实例访问父类的name
};
return Employee;
}(Person));
var howard = new Employee("Howard", "sales");
console.log(howard.getElevatorPitch());
//console.log(howard.name); //访问父类的,失败,不能直接被访问,但是能被派生方法所访问
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map// 构造函数使用保护
class Person {
protected name: string;
protected constructor(theName:string){ // 构造方法,进行保护
this.name = theName;
}
}
class Employee extends Person {
private department: string;
constructor(name: string, department:string){
super(name);
this.department = department;
}
public getElevatorPitch() {
return "hello" + this.department + this.name;
}
}
let howard = new Employee("Howard", "Sales");
//let john = new Peron("John"); //错误,构造函数被保护,不能在外部访问var __extends = (this && this.__extends) || (function () {
var extendStatics = function (d, b) {
extendStatics = Object.setPrototypeOf ||
({ __proto__: [] } instanceof Array && function (d, b) { d.__proto__ = b; }) ||
function (d, b) { for (var p in b) if (b.hasOwnProperty(p)) d[p] = b[p]; };
return extendStatics(d, b);
}
return function (d, b) {
extendStatics(d, b);
function __() { this.constructor = d; }
d.prototype = b === null ? Object.create(b) : (__.prototype = b.prototype, new __());
};
})();
// 构造函数使用保护
var Person = /** @class */ (function () {
function Person(theName) {
this.name = theName;
}
return Person;
}());
var Employee = /** @class */ (function (_super) {
__extends(Employee, _super);
function Employee(name, department) {
var _this = _super.call(this, name) || this;
_this.department = department;
return _this;
}
Employee.prototype.getElevatorPitch = function () {
return "hello" + this.department + this.name;
};
return Employee;
}(Person));
var howard = new Employee("Howard", "Sales");
//let john = new Peron("John"); //错误,构造函数被保护,不能在外部访问
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.mapreadonly修饰符
将属性设置为只读
class Octopus {
readonly name: string; // 只读
readonly numberOfLegs: number = 8; // 只读
constructor(theName:string){
this.name = theName;
}
}
let dad = new Octopus("Hello world");
//dad.name = "Hello world"; //设置值。出错,由于为只读var Octopus = /** @class */ (function () {
function Octopus(theName) {
this.numberOfLegs = 8; // 只读
this.name = theName;
}
return Octopus;
}());
var dad = new Octopus("Hello world");
//dad.name = "Hello world"; //设置值。出错,由于为只读
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map参数属性
class Octopus {
readonly numberOfLegs: number = 9;
constructor(readonly name:string){ // 直接定义参数属性
}
}var Octopus = /** @class */ (function () {
function Octopus(name) {
this.name = name;
this.numberOfLegs = 9;
}
return Octopus;
}());
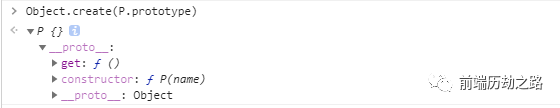
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map通过get set获取属性
let passcode = "secret passcode";
class Employee {
private _fullName: string; // 保护成员一般下划线
get fullName():string { // get方法
return this._fullName;
}
set fullName(newName:string){
if (passcode && passcode == "code") {
// 进行赋值操作
this._fullName = newName;
}else {
console.log("出现重复")
}
}
}
let employee = new Employee(); // 创建对象
employee.fullName = "Bob"; //调用get方法
// 下面调用set方法
if(employee.fullName){
console.log(employee.fullName);
}
PS C:\Users\mingm\Desktop\ts> tsc
Active code page: 65001
PS C:\Users\mingm\Desktop\ts>var passcode = "secret passcode";
var Employee = /** @class */ (function () {
function Employee() {
}
Object.defineProperty(Employee.prototype, "fullName", {
get: function () {
return this._fullName;
},
set: function (newName) {
if (passcode && passcode == "code") {
// 进行赋值操作
this._fullName = newName;
}
else {
console.log("出现重复");
}
},
enumerable: true,
configurable: true
});
return Employee;
}());
var employee = new Employee(); // 创建对象
employee.fullName = "Bob"; //调用get方法
// 下面调用set方法
if (employee.fullName) {
console.log(employee.fullName);
}
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map只能输出es5或更高的版本,不支持输出es3
静态属性
当类未被实例化的时候,可以直接访问的为静态属性
class Grid {
static origin = { x: 0, y: 0 }; // 这里类似使用static
calculate(point:{x:number, y:number}){ // 在此处定义了point,
let x = point.x - Grid.origin.x // 前面访问的是poinyt定义的,后面访问的是static定义的origin
let y = point.y - Grid.origin.y; // 同理如上
return point.x + point.y;
}
constructor(public scale: number) { };
}
let grid1 = new Grid(1.0);// 对static进行赋值
let grid2 = new Grid(2.0);
// 访问
grid1.calculate({x:10, y:10});
grid2.calculate({x:10, y:10});
var Grid = /** @class */ (function () {
function Grid(scale) {
this.scale = scale;
}
Grid.prototype.calculate = function (point) {
var x = point.x - Grid.origin.x; // 前面访问的是poinyt定义的,后面访问的是static定义的origin
var y = point.y - Grid.origin.y; // 同理如上
return point.x + point.y;
};
;
Grid.origin = { x: 0, y: 0 }; // 这里类似使用static
return Grid;
}());
var grid1 = new Grid(1.0); // 对static进行赋值
var grid2 = new Grid(2.0);
// 访问
grid1.calculate({ x: 10, y: 10 });
grid2.calculate({ x: 10, y: 10 });
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map抽象类
抽象类为其他派生类的基类。
抽象类不会被实例化
抽象类用于作为基类,派生出其他类使用。
// 定义抽象类
abstract class Department {
constructor(public name:string){
}
// 定义实现的细节
printName():void{
console.log("实现细节");
}
// 定义抽象方法,该抽象方法必须在派生类中实现其具体的内容
abstract printMeeting(): void;
}
class AccountingDepartemnt extends Department {
constructor(){
super("hello world"); // 调用基类的构造方法
}
// 对抽象方法进行完善
printMeeting():void{
console.log("完善!");
}
// 定义其余的方法
generateReports():void{
console.log("添加的其他方法")
}
}
// 创建一个抽象类型的引用
let department: Department; // 抽象类的引用,类似于定义,可以被抽象类的子类进行实例化,即分配内存空间,不能被抽象类进行实例化,因为抽象类不能分配内存空间,所以不能对抽象类进行new操作
department = new AccountingDepartemnt(); // 可以进行分配内存空间
department.printMeeting(); var __extends = (this && this.__extends) || (function () {
var extendStatics = function (d, b) {
extendStatics = Object.setPrototypeOf ||
({ __proto__: [] } instanceof Array && function (d, b) { d.__proto__ = b; }) ||
function (d, b) { for (var p in b) if (b.hasOwnProperty(p)) d[p] = b[p]; };
return extendStatics(d, b);
}
return function (d, b) {
extendStatics(d, b);
function __() { this.constructor = d; }
d.prototype = b === null ? Object.create(b) : (__.prototype = b.prototype, new __());
};
})();
// 定义抽象类
var Department = /** @class */ (function () {
function Department(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 定义实现的细节
Department.prototype.printName = function () {
console.log("实现细节");
};
return Department;
}());
var AccountingDepartemnt = /** @class */ (function (_super) {
__extends(AccountingDepartemnt, _super);
function AccountingDepartemnt() {
return _super.call(this, "hello world") || this;
}
// 对抽象方法进行完善
AccountingDepartemnt.prototype.printMeeting = function () {
console.log("完善!");
};
// 定义其余的方法
AccountingDepartemnt.prototype.generateReports = function () {
console.log("添加的其他方法");
};
return AccountingDepartemnt;
}(Department));
// 创建一个抽象类型的引用
var department; // 抽象类的引用,类似于定义,可以被抽象类的子类进行实例化,即分配内存空间,不能被抽象类进行实例化,因为抽象类不能分配内存空间,所以不能对抽象类进行new操作
department = new AccountingDepartemnt(); // 可以进行分配内存空间
department.printMeeting();
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map构造函数
可以使用类似于java中的语法,进行声明构造函数
class Greeter{
greeting: string;
constructor(message:string){
this.greeting = message;
}
// 类似于java中声明构造方法
greet(){
return "hello " + this.greeting;
}
}
// 首先进行创建引用,类似于原生的var,仅仅声明,并未创建引用。但是必须进行声明,声明其为Greeter
let greeter: Greeter;
// 进行分配空间
greeter = new Greeter("world");
console.log(greeter.greet());和使用抽象接口一样,当使用抽象接口的时候,必须要进行先创建引用,然后在分配空间
原生的如下
var i; // 在栈上开辟一块空间,进行储存
i = new Greeter(); // 完成由栈到堆的指向,对象储存在堆中,当然啦,C++允许对象储存在栈中必须进行两步。
关于C++堆和栈的类
静态建立
使用
Box Box如上的方式,将会静态的建立一个对象
静态建立对象,将会由编译器在栈中分配内存空间。通过移动栈顶指针,挪出适当的位置,在内存空间上调用构造函数,形成一个栈对象,此方法为在栈中储存对象。
动态建立
使用
Box* Box = new Box();如上的方式,将会动态的建立一个对象。
使用new操作运算符的时候,将会在堆中分配一块内存空间,完成由栈到对的指向。
类当做接口使用
接口,一种传入对象的规范,比喻,水管的水龙头。
类可以创建出任何类型
class Point{
x: number;
y: number;
}
interface Point3d extends Point{
z: number;
}
let point3d:Point3d = {
x:1,
y:2,
z:4
}使用extends,进行创建接口
var Point = /** @class */ (function () {
function Point() {
}
return Point;
}());
var point3d = {
x: 1,
y: 2,
z: 4
};
//# sourceMappingURL=out.js.map