算法,就是计算机处理信息的一个步骤。是独立存在的一种处理问题的方法和思想,并不局限于具体的实现过程。
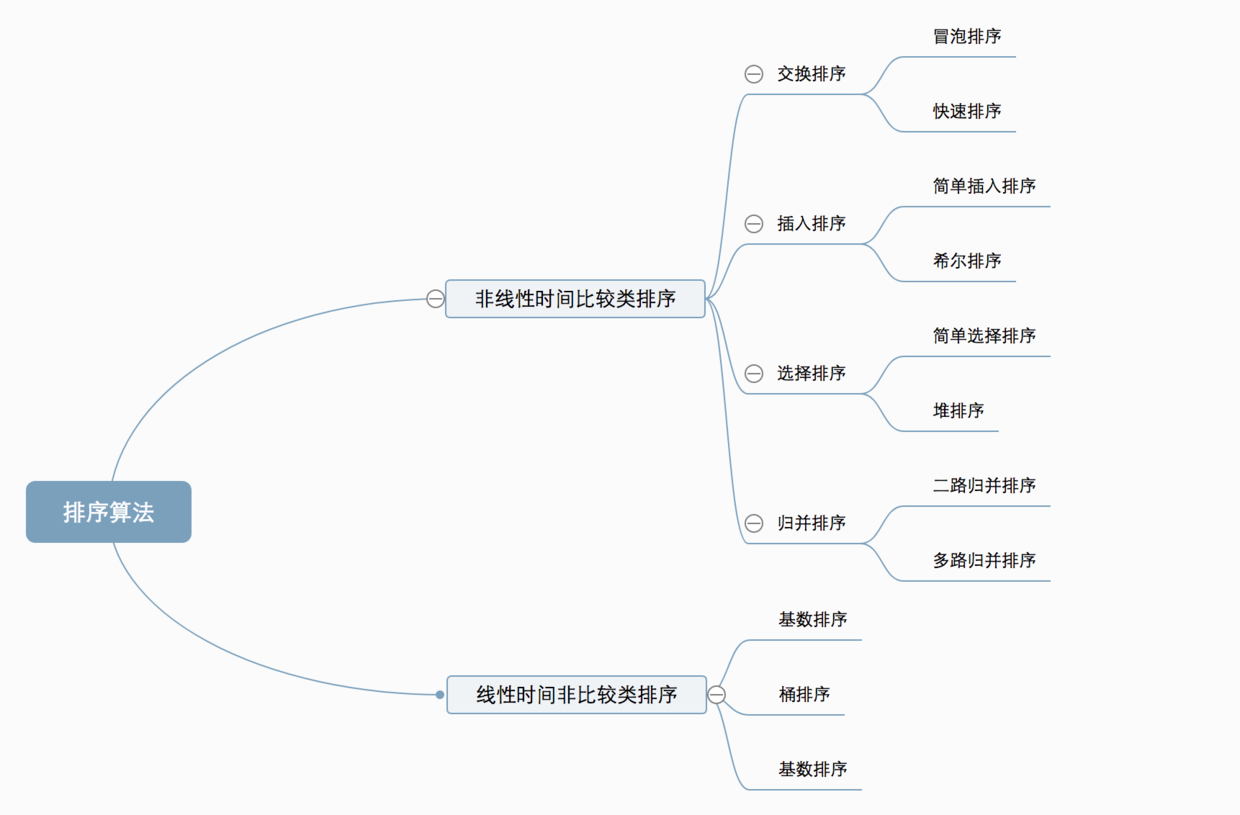
排序
冒泡
public static int[] BubbleSort (int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
选择
public static int[] SelectSort (int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length-1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < arr.length; j++) {
int temp = arr[i];
if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = temp;
}
}
}
return arr;
}
快排
public int[] MySort (int[] arr) {
quicksort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
return arr;
}
public void quicksort(int[] list, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int pivot = randompivot(list, left, right);
quicksort(list,left, pivot-1);
quicksort(list, pivot+1, right);
}
}
public int randompivot(int[] list, int left, int right) {
int first = list[left];
while (left < right) {
while (left < right && list[right] >= first) {
right--;
}
swap(list, left, right);
while(left<right && list[left] <= first) {
left++;
}
swap(list, left, right);
}
return left;
}
public void swap(int[] list, int left, int right) {
int temp = list[left];
list[left] = list[right];
list[right] = temp;
}堆排序
二分查找
复杂度 O(log2n)
public static int search(int[] nums, int target) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return -1;
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left < right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (nums[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
} else {
right = mid;
}
}
return nums[left] == target ? left : -1;
}栈与队列
用栈实现队列
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
//如果 outstack 是空的,就把instack 全部 push 到 outstack 里
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
// 否则直接弹出
return stack2.pop();
}
}字符串
最长无重复子串
public int maxLength(int[] arr) {
//用链表实现队列,队列是先进先出的
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
int res = 0;
for (int c : arr) {
while (queue.contains(c)) {
//如果有重复的,队头出队
queue.poll();
}
//添加到队尾
queue.add(c);
res = Math.max(res, queue.size());
}
return res;
}数组
斐波那契数列
递归
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return n;
return Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2);
}非归递
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return n;
int first = 0;
int second = 1;
int temp;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
temp = second;
second = first + second;
first = temp;
}
return second;
}有序数组合并
public void merge(int A[], int m, int B[], int n) {
int aPtr = m - 1, bPtr = n - 1;
// 两数组元素从右至左比较,大的去 A 尾部,直至有一方指针到头为止
for (int ptr = m + n - 1; aPtr >= 0 && bPtr >= 0; ptr--){
A[ptr] = A[aPtr] > B[bPtr] ? A[aPtr--] : B[bPtr--];
}
// A 指针先走完的情况,B 中剩余元素直接copy至 A 对应位置即可;
while (bPtr >= 0){
A[bPtr] = B[bPtr--];
}
}两数之和
public int[] twoSum (int[] numbers, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int index = 0; index < numbers.length; index++) {
int cur = numbers[index];
if (map.containsKey(target-cur)) {
return new int[]{map.get(target-cur)+1, index+1};
}
map.put(cur, index);
}
throw new RuntimeException("results not exits");
}移除有序数组中的重复元素
链表
链表翻转
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode next = null;
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;//先找 next 指针
cur.next = pre;//往前指
pre = cur;//往后平移
cur = next;//往后平移
}
return pre;
}判断是否有环
public class Solution {
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) return false;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
while (fast != null && fast.next !=null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
if (fast == slow) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}链表中环的入口节点
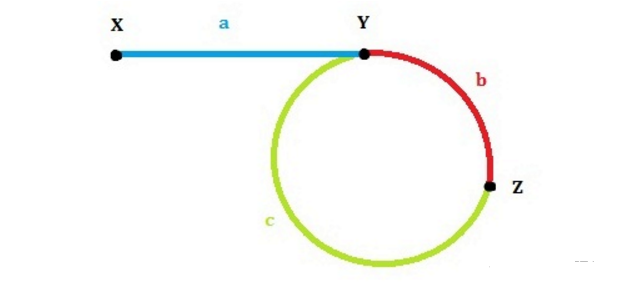
- 那么我们可以知道fast指针走过a+b+c+b
- slow指针走过a+b
- 那么 2*(a+b) = a+b+c+b
- 所以a = c
- 那么此时让 fast 回到起点,slow 依然停在z,两个同时开始走,一次走一步
- 那么它们最终会相遇在y点,正是环的起始点
public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { if (head == null || head.next == null) return null; ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next !=null) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next.next; if (fast == slow) { fast = head;// fast回到起点 while (fast != slow) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; } return slow; } } return null; } }链表中倒数第K个节点
1.先让first指针先走 K 步 2.再让first和second指针同时走,first指针走到尾,则second相当于走到倒数第k个节点
public ListNode FindKthToTail (ListNode pHead, int k) {
if (pHead == null) return pHead;
ListNode first = pHead;
while (k-- > 0) {
if (first == null) return null;
first = first.next;
}
ListNode second = pHead;
while (first != null) {
first = first.next;
second = second.next;
}
return second;
}合并有序链表
归递
public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null || l2 == null) {
return l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
}
ListNode first = l1.val < l2.val ? l1 : l2;
first.next = mergeTwoLists(first.next, first == l1 ? l2 : l1);
return first;
}非递归
public ListNode mergeTwoLists (ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val > l2.val) {
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
} else {
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return dummy.next;
}两个链表的第一个公共结点
1、假设 链表A 长度为 a,链表B长度为 b, 2、A 走完 a 再将指针指向B 和 B走完b 再将指针指向A,那肯定会相遇; 3、即 a+c+b = b+c+a; (公共点后长度为 c)
此题和链表入口环的节点 题目题解一样的思路。
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
if (pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) return null;
ListNode p1 = pHead1;
ListNode p2 = pHead2;
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = p1 != null ? p1.next : pHead2;//到头了就指向 B
p2 = p2 != null ? p2.next : pHead1;//到头了就指向 A
}
return p1;
}二叉树
判断是否是完全二叉树
public boolean isFull(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return false;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
boolean isLeaf = false;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (isLeaf && !isLeaf(node)) {
return false;
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node);
} else if (node.right != null) {
return false;
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node);
} else {
isLeaf = true;
}
}
return true;
}
private boolean isLeaf(TreeNode node) {
return (node.left == null) && (node.right == null);
}二叉树高度
归递
public int maxDepth (TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
return 1+ Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right));
}层序遍历
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> levelOrder (TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return new ArrayList();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
ArrayList subList = new ArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < size;i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
subList.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
list.add(subList);
}
return list;
}之字形层序遍历
public ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> zigzagLevelOrder (TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return new ArrayList();
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ArrayList sublist = new ArrayList();//存储每一层节点
for (int i = queue.size(); i >0;i--) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();//弹出队列中的节点
if ((list.size()+1) %2 !=0) {//奇数层,尾部插入
sublist.add(node.val);
} else {//偶数层 头插
sublist.add(0, node.val);
}
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
list.add(sublist);
}
return list;
}二叉树翻转
public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode temp = node.left;
node.left = node.right;
node.right = temp;
invertTree(node.left);
invertTree(node.right);
return node;
}











