前言:笔者把学习的webpack知识从基础到原理写个系列,以便回顾。希望能帮助到更多正在学习webpack的小伙伴。
定义
loader只是一个导出为函数的js模块
结构
一个最简单的loader代码结构:
module.exports = function(source){
return source;
}多个loader执行顺序
执行顺序是串行执行,从右向左
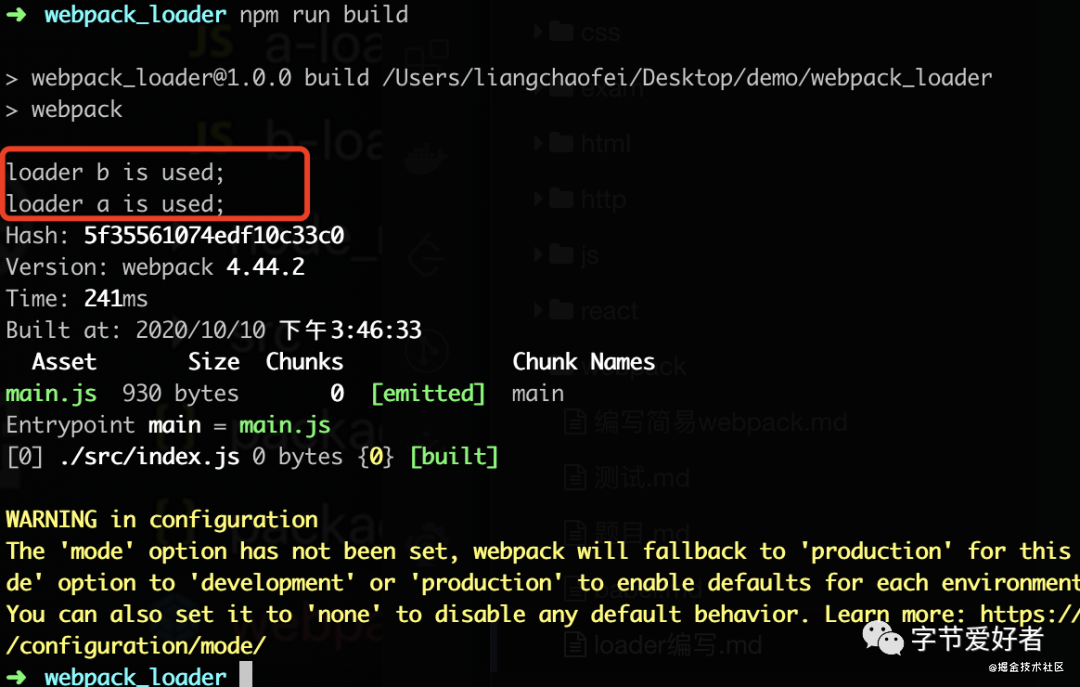
通过一个例子进行验证loader执行顺序
- 1.在webpack.config.js中先后配置a-loader和b-loader
// webpack.config.js const path = require('path');
module.exports = { entry: './src/index.js', output: { path: path.join(__dirname, 'dist'), filename: 'main.js', }, module: { rules: [ { test: /.js$/, use: [path.resolve('./loaders/a-loader.js'), path.resolve('./loaders/b-loader.js')], }, ], }, };
+ 2.分别写下a-loader.js和b-loader.js
```js
// a-loader.js
module.exports = function a(source) {
console.log('loader a is used;');
return source;
};
// b-loader.js
module.exports = function b(source) {
console.log('loader b is used;');
return source;
};- 3.运行web pack,可以看出先打印了b,再打印了a
loader调试利器:loader-runner
定义:
loader-runner 允许在不安装webpack的情况下运行loaders
作用:
作为webpack的依赖,webpack中使用它执行loader,进行loader的开发和调试
loader-runner的使用
import { runLoaders } from "loader-runner";
runLoaders({
resource: "/abs/path/to/file.txt?query",
// String: 资源的绝对路径(可以增加查询字符串)
loaders: ["/abs/path/to/loader.js?query"],
// String[]: loader的绝对路径(可以增加查询字符串)
context: { minimize: true },
// 基础上下文之外的额外loader上下文
readResource: fs.readFile.bind(fs)
// 读取资源的函数
}, function(err, result) {
// err: Error?
})下面使用loader-runner开发一个raw-loader(将一个文件内容转换为string)
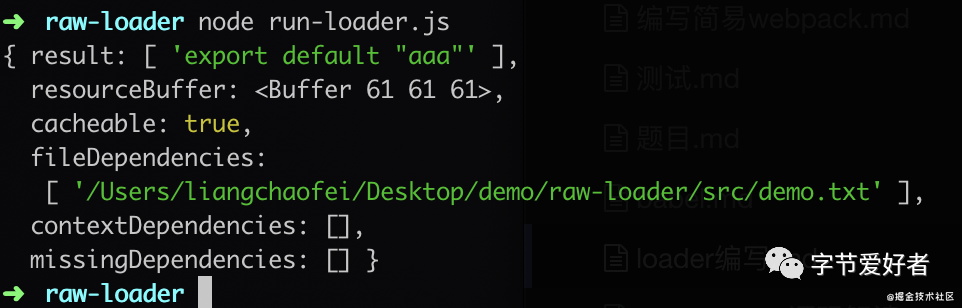
1.编写raw-loader和测试用例
// src/raw-loader.js
module.exports = function (source) {
const json = JSON.stringify(source)
.replace(/\u2028/g, '\\u2028')
.replace(/\u2029/g, '\\u2029');
return `export default ${json}`;
};
// src/demo.txt
aaa2.使用run-loader
// /run-loader.js
const { runLoaders } = require('loader-runner');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
runLoaders(
{
resource: path.join(__dirname, './src/demo.txt'),
loaders: [path.join(__dirname, './src/raw-loader.js')],
context: {
minimize: true,
},
readResource: fs.readFile.bind(fs),
},
(err, res) => {
err ? console.log(err) : console.log(res);
}
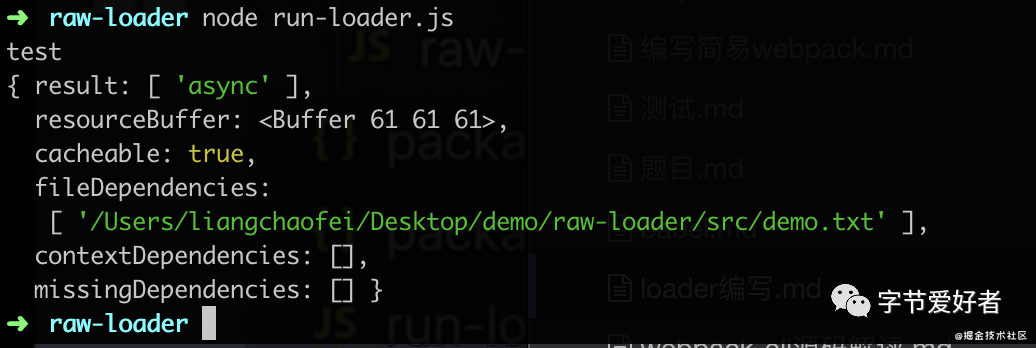
);3.运行node run-loader.js,可以看出结果
获取loader参数
使用loader-utils包。先安装下。
npm i loader-utils -S在run-loader.js中引入一个参数,如下:
loaders: [
{
loader: path.join(__dirname, './src/raw-loader.js'),
options: {
name: 'test',
},
},
],接着在raw-loader.js中使用loader-utils获取参数
const loaderUtils = require('loader-utils');
module.exports = function (source) {
const { name } = loaderUtils.getOptions(this);
console.log(name);
const json = JSON.stringify(source)
.replace(/\u2028/g, '\\u2028')
.replace(/\u2029/g, '\\u2029');
return `export default ${json}`;
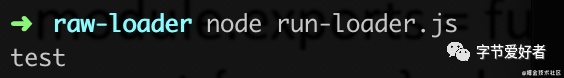
};打印下name,查看结果
loader的异常处理
1.loader内直接通过throw抛出
2.通过this.callback传递错误
this.callback(
err: Error | null,
content: string | Buffer,
sourceMap?: SourceMap,
meta?: any
)如何开发一个异步的loader
通过 this.async来返回一个异步函数。第一个参数是Error, 第二个参数是处理的结果
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
module.exports = function (source) {
const callback = this.async();
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, './async.txt'), 'utf-8', (err, data) => {
callback(null, data);
});
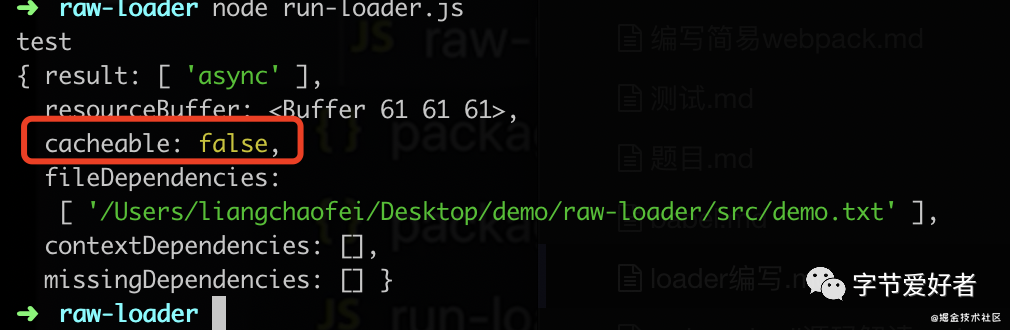
};运行打印,可以看到是异步结果
在loader中使用缓存:
1.webpack中默认开启loader缓存,可以使用this.cacheable(false)关闭缓存
2.缓存条件:loader的结果在相同的输入下有确定的输出。有依赖的loader无法使用缓存。