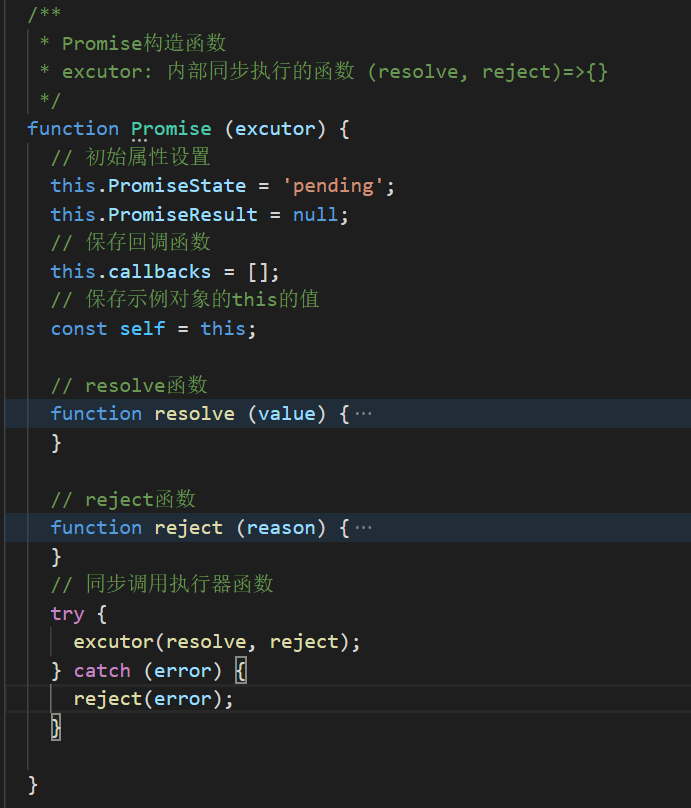
Promsie js实现
step 1
初始化promise对象:
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise {
/**
*
* @param {Function} fn (resolve, reject)
*/
constructor(fn){
// 初始状态为pending
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
}
resolve(value){
}
reject(resaon){
}
}step 2
实现resolve 和 reject方法
/**
*
* @param {Function} fn (resolve, reject)
*/
constructor(fn){
// 初始状态为pending
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
try{
fn(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this)); // 为什么需要 bind(this) ?
// 传入的fn可能是一个普通的函数,并不是箭头函数,有他自己的执行环境
}catch(e){
this.reject(e);
}
}
resolve(value){
// 判断状态 只有PENDING才可以修改状态
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
}
}
reject(resaon){
// 判断状态 只有PENDING才可以修改状态
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.resaon = resaon;
this.status = REJECTED;
}
}step 3
then方法的实现
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
// 添加兜底函数
const realOnFulfilled = this.isFunction(onFulfilled) ? onFulfilled : (value) => {
return value;
};
const realOnRejected = this.isFunction(onRejected) ? onRejected : (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
// .then的返回值整体是一个promise
const promise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
switch(this.status){
case FULFILLED: {
realOnFulfilled();
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
realOnRejected();
break;
}
}
})
return promise;
}
// 工具函数 判断是否function
isFunction(value){
return typeof value === 'function'
}需要考虑到promise内部如果是一个异步resolve或者reject方法的情况,此时状态仍是pending.
// 添加两个数组,存储一部resolve reject方法
FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
//...
// .then的返回值整体是一个promise
const promise = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
switch(this.status){
// ...
case PENDING: {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(realOnFulfilled);
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(realOnRejected);
break;
}
}
})
return promise;
}那么如何去维护FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST这两个数组,到底什么时候去掉用呢?
可以使用es6的get和set去维护
// 添加一个新的变量来维护状态
_status = PENDING;
get status(){
return this._status;
}
set status(newStatus){
this._status = newStatus;
switch(newStatus){
case FULFILLED: {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback => {
callback(this.value);
})
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback => {
callback(this.resaon);
})
break;
}
}
}根据promiseA+规范 onFulfilled 和 onRejected执行的异常,promsie需要被rejected,并且执行结果需调用resolvePromise方法,所以需要对realOnFulfilled 和 realOnRejected函数添加try catch捕获异常,调用resolvePromise
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
// ...
// .then的返回值整体是一个promise
const promise2 = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
// onFulfilled 和 onRejected执行的异常,promsie需要被rejected
const fulfilledMircotask = () => {
try{
const x = realOnFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
const rejectedMircotask = () => {
try{
const x = realOnRejected(this.resaon);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
}
switch(this.status){
case FULFILLED: {
fulfilledMircotask();
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
rejectedMircotask();
break;
}
case PENDING: {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(fulfilledMircotask);
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(fulfilledMircotask);
break;
}
}
})
return promise2;
}
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject){
}promise中onFulfilled, onRejected为微任务,使用queueMicroTask进行包裹
const promise2 = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
const fulfilledMircotask = () => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try{
const x = realOnFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
})
}
const rejectedMircotask = () => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try{
const x = realOnRejected(this.resaon);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
})
}
// ...
}) step 4
实现resolvePromise方法
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject){
// 如果x promise相等
if(promise2 === x){
return reject(new TypeError('the promise and the return value are the same'))
}
// 如果x是一个promsie 那么让新的promise接口x的状态
// 那继续执行x,如果执行的时候又返回了一个y,那么继续解析y
if(x instanceof MPromise){
// 这里也是执行了promise 需要queueMicrotask包裹下
queueMicrotask(() => {
x.then(y => {
this.resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject);
}, reject);
})
}else if(typeof x === 'object' || this.isFunction(x)){
if(x === null){
return reject(x);
}
let then = null;
try{
// 去x.then的值赋值给then
then = x.then;
}catch(e){
return reject(e);
}
// 如果获取的then是一个函数
if(this.isFunction(then)){
// flag 确保只被执行一次
let called = false;
try{
then.call(
x,
(y) => {
if(called){
return;
}
called = true;
this.resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject);
},
(r) => {
if(called){
return;
}
called = true;
reject(r);
}
)
}catch(err){
if(called){
return;
}
reject(err);
}
}else{
resolve(x);
}
}else{
resolve(x)
}
}step 5
catch方法实现就很简单了
catch(onRejected){
this.then(null, onRejected);
}step 6
除了这些 promsie还有一些静态方法,eg resolve reject。 什么是静态方法?
static resolve(value){
if(value instanceof MPromise){
return value;
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(value);
})
}
static reject(reason){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(reason);
})
}
// race状态是依托内部执行最快的那个状态
static race(promiseList){
if(!Array.isArray(promiseList)){
return
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(promiseList.length === 0){
resolve();
}else{
promiseList.forEach(promise => {
MPromise.resolve(promise).then(
val => resolve(val),
reason => reject(reason)
)
})
}
})
}
static all(promiseList){
if(!Array.isArray(promiseList)){
return
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(promiseList.length === 0){
resolve([]);
}else{
let count = [];
let res = [];
promiseList.forEach((promise, index) => {
MPromise.resolve(promise).then(
val => {
res[index] = val;
count++;
if(count === promiseList.length){ // 可否用 index === promiseList.length 来做判断 为什么?
resolve(res)
}
},
reason => reject(reason)
)
})
}
})
}
// ...完整代码
const PENDING = 'pending';
const FULFILLED = 'fulfilled';
const REJECTED = 'rejected';
class MPromise {
// 添加两个数组,存储一部resolve reject方法
FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST = [];
_status = PENDING;
/**
* @param {Function} fn (resolve, reject)
*/
constructor(fn){
// 初始状态为pending
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = null;
this.reason = null;
try{
fn(this.resolve.bind(this), this.reject.bind(this)); // 为什么需要 bind(this) ?
// 传入的fn可能是一个普通的函数,并不是箭头函数,有他自己的执行环境
}catch(e){
this.reject(e);
}
}
resolve(value){
// 判断状态 只有PENDING才可以修改状态
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.value = value;
this.status = FULFILLED;
}
}
reject(resaon){
// 判断状态 只有PENDING才可以修改状态
if(this.status === PENDING){
this.resaon = resaon;
this.status = REJECTED;
}
}
get status(){
return this._status;
}
set status(newStatus){
this._status = newStatus;
switch(newStatus){
case FULFILLED: {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback => {
callback(this.value);
})
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.forEach(callback => {
callback(this.resaon);
})
break;
}
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected){
// 添加兜底函数
const realOnFulfilled = this.isFunction(onFulfilled) ? onFulfilled : (value) => {
return value;
};
const realOnRejected = this.isFunction(onRejected) ? onRejected : (reason) => {
throw reason;
};
// .then的返回值整体是一个promise
const promise2 = new MPromise((resolve, reject) => {
// onFulfilled 和 onRejected执行的异常,promsie需要被rejected
const fulfilledMircotask = () => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try{
const x = realOnFulfilled(this.value);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
})
}
const rejectedMircotask = () => {
queueMicrotask(() => {
try{
const x = realOnRejected(this.resaon);
this.resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
}catch(e){
reject(e);
}
})
}
switch(this.status){
case FULFILLED: {
fulfilledMircotask();
break;
}
case REJECTED: {
rejectedMircotask();
break;
}
case PENDING: {
this.FULFILLED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(fulfilledMircotask);
this.REJECTED_CALLBACK_LIST.push(fulfilledMircotask);
break;
}
}
})
return promise2;
}
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject){
// 如果x promise相等
if(promise2 === x){
return reject(new TypeError('the promise and the return value are the same'))
}
// 如果x是一个promsie 那么让新的promise接口x的状态
// 那继续执行x,如果执行的时候又返回了一个y,那么继续解析y
if(x instanceof MPromise){
// 这里也是执行了promise 需要queueMicrotask包裹下
queueMicrotask(() => {
x.then(y => {
this.resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject);
}, reject);
})
}else if(typeof x === 'object' || this.isFunction(x)){
if(x === null){
return reject(x);
}
let then = null;
try{
// 去x.then的值赋值给then
then = x.then;
}catch(e){
return reject(e);
}
// 如果获取的then是一个函数
if(this.isFunction(then)){
// flag 确保只被执行一次
let called = false;
try{
then.call(
x,
(y) => {
if(called){
return;
}
called = true;
this.resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject);
},
(r) => {
if(called){
return;
}
called = true;
reject(r);
}
)
}catch(err){
if(called){
return;
}
reject(err);
}
}else{
resolve(x);
}
}else{
resolve(x)
}
}
catch(onRejected){
this.then(null, onRejected);
}
static resolve(value){
if(value instanceof MPromise){
return value;
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve(value);
})
}
static reject(reason){
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
reject(reason);
})
}
// race状态是依托内部执行最快的那个状态
static race(promiseList){
if(!Array.isArray(promiseList)){
return
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(promiseList.length === 0){
resolve();
}else{
promiseList.forEach(promise => {
MPromise.resolve(promise).then(
val => resolve(val),
reason => reject(reason)
)
})
}
})
}
static all(promiseList){
if(!Array.isArray(promiseList)){
return
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if(promiseList.length === 0){
resolve([]);
}else{
let count = [];
let res = [];
promiseList.forEach((promise, index) => {
MPromise.resolve(promise).then(
val => {
res[index] = val;
count++;
if(count === promiseList.length){ // 可否用 index === promiseList.length 来做判断 为什么?
resolve(res)
}
},
reason => reject(reason)
)
})
}
})
}
// 工具函数 判断是否function
isFunction(value){
return typeof value === 'function'
}
}