@Autowired注解的实现过程,其实就是Spring Bean的自动装配过程。通过看@Autowired源码注释部分我们可以看到@Autowired的实现是通过AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器中实现的。
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 类图
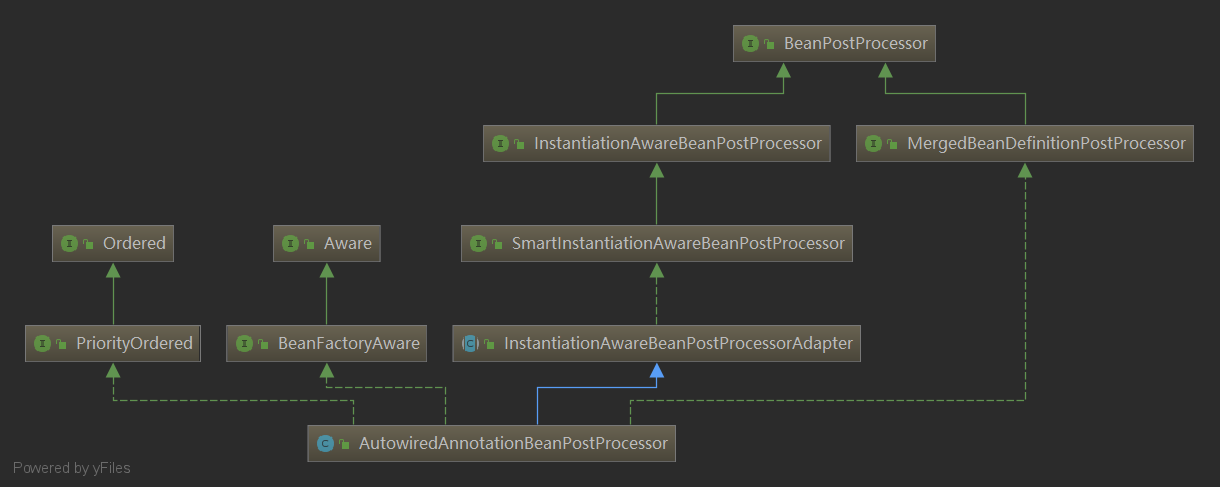
- PriorityOrdered:确认
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器的执行优先级 - BeanFactoryAware:使得
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor可以直接通过BeanFactory获取容器中的Bean - BeanPostProcessor:在 Bean 初始化前后执行的后置处理器
- InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor:在 Bean 实例化前后和Bean设置属性值时执行的后置处理器
- SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor:智能实例化Bean的后处理器,如预测Bean的类型和确认Bean的构造函数等。
- MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor:合并Bean的定义信息。
在分析自动装配前我们先来介绍一下上面的这些后置处理器。
后置处理器介绍
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor有两个方法,postProcessBeforeInitialization和postProcessAfterInitialization。它们分别在任何bean初始化回调之前或之后执行(例如InitializingBean的afterPropertiesSet方法或自定义init-method方法之前或者之后), 在这个时候该bean的属性值已经填充完成了,并且我们返回的bean实例可能已经是原始实例的包装类型了。例如返回一个FactoryBean。
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor继承自BeanPostProcessor接口。主要多提供了以下三个方法。
postProcessBeforeInstantiation
该方法是在Bean实例化目标对象之前调用,返回的Bean对象可以代理目标,从而有效的阻止了目标Bean的默认实例化。
protected Object resolveBeforeInstantiation(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
Object bean = null;
if (!Boolean.FALSE.equals(mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved)) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
Class<?> targetType = determineTargetType(beanName, mbd);
if (targetType != null) {
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(targetType, beanName);
if (bean != null) {
// 如果此方法返回一个非null对象,则Bean创建过程将被短路。
// 唯一应用的进一步处理是来自已配置BeanPostProcessors的postProcessAfterInitialization回调
bean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
}
}
mbd.beforeInstantiationResolved = (bean != null);
}
return bean;
}
protected Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 执行Bean实例化目标对象之前的后置处理方法
Object result = ibp.postProcessBeforeInstantiation(beanClass, beanName);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
}
}
return null;
}
跟进源码我们可以看出,如果此方法返回一个非null对象,则Bean创建过程将被短路。唯一应用的进一步处理是来自已配置BeanPostProcessors的postProcessAfterInitialization回调。
postProcessAfterInstantiation
该方法执行在通过构造函数或工厂方法在实例化bean之后但在发生Spring属性填充(通过显式属性或自动装配)之前执行操作。这是在Spring的自动装配开始之前对给定的bean实例执行自定义字段注入的理想回调。如果该方法返回false,那么它会阻断后续InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor后置处理器的执行,并且会阻止后续属性填充的执行逻辑。
postProcessPropertyValues
在工厂将给定属性值应用于给定bean之前,对它们进行后处理。允许检查是否满足所有依赖关系,例如基于bean属性设置器上的“ Required”注解。还允许替换要应用的属性值,通常是通过基于原始PropertyValues创建新的MutablePropertyValues实例,添加或删除特定值来实现。
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
智能实例化Bean的后处理器,主要提供了三个方法。
predictBeanType
预测从此处理器的postProcessBeforeInstantiation回调最终返回的bean的类型。
determineCandidateConstructors
确定使用实例化Bean的构造函数。
getEarlyBeanReference
获取提早暴露的Bean的引用,提早暴露的Bean就是只完成了实例化,还未完成属性赋值和初始化的Bean。
MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
postProcessMergedBeanDefinition
合并Bean的定义信息的后处理方法,该方法是在Bean的实例化之后设置值之前调用。
自动装配的实现
找到需要自动装配的元素
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器主要负责对添加了@Autowired和@Value注解的元素实现自动装配。所以找到需要自动装配的元素,其实就是对@Autowired和@Value注解的解析。
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器,找出需要自动装配的元素是在MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition这个方法中实现的,调用链路如下:
doWith:445, AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$2 (org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation)
doWithLocalFields:657, ReflectionUtils (org.springframework.util)
buildAutowiringMetadata:433, AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor (org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation)
findAutowiringMetadata:412, AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor (org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation)
postProcessMergedBeanDefinition:235, AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor (org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation)
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors:1000, AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
doCreateBean:523, AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
createBean:483, AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
getObject:312, AbstractBeanFactory$1 (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
getSingleton:230, DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
doGetBean:308, AbstractBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
getBean:197, AbstractBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
preInstantiateSingletons:761, DefaultListableBeanFactory (org.springframework.beans.factory.support)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization:867, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
refresh:543, AbstractApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.support)
<init>:84, AnnotationConfigApplicationContext (org.springframework.context.annotation)
从链路上我们可以看到,找到需要自动装配的元素是在findAutowiringMetadata方法中实现的,该方法会去调用buildAutowiringMetadata方法构建元数据信息。如果注解被加载属性上将会被封装成AutowiredFieldElement对象;如果注解加在方法上,那么元素会被封装成AutowiredMethodElement对象。这里两个对象的inject方法将最后完成属性值的注入,主要区别就是使用反射注入值的方式不一样。源码如下:
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
// 存放我们找到的元数据信息
final LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements =
new LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement>();
// 通过反射找出对应Class对象的所有Field
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, new ReflectionUtils.FieldCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Field field) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
// 通过反射找到该字段上所有的注解信息,并判断是否有@Autowired和@Value注解,如果有就将该字段封成AutowiredFieldElement对象
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);、
// 将该字段封成AutowiredFieldElement对象,并放到缓存中
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
}
});
// 通过反射找出对应Class对象的所有Method
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() {
@Override
public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException {
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (!BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
return;
}
// 通过反射找到该字段上所有的注解信息,并判断是否有@Autowired和@Value注解,如果有就将该字段封成AutowiredMethodElement对象
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
return;
}
if (method.getParameterTypes().length == 0) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation should only be used on methods with parameters: " +
method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
// 将该字段封成AutowiredMethodElement对象
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
}
});
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
// 循环处理父类需要自动装配的元素
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
// 将需要自动装配的元素封装成InjectionMetadata对象,最后合并到Bean定义中
return new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements);
}
寻找需要自动装配过程:
- 根据Class对象,通过反射获取所有的
Field和```Method````对象 - 通过反射获取
Field和Method上的注解,并判断是否有@Autowired和@Value注解 - 将注解了@Autowired和@Value的
Field和Method封装成AutowiredFieldElement和AutowiredMethodElement对象,等待下一步的自动装配。 - 循环处理父类需要自动装配的元素
- 将需要自动装配的元素封装成InjectionMetadata对象,最后合并到Bean定义的
externallyManagedConfigMembers属性中
注入属性值
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor后置处理器注入属性值是在postProcessPropertyValues方法中实现的。源码如下:
public void inject(Object target, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
// 获取需要自动装配的元数据信息(这里实在缓存中取)
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(this.checkedElements != null ? this.checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
// 调用AutowiredFieldElement或AutowiredMethodElement对象的inject方法注入属性值
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
AutowiredFieldElement#inject
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<String>(1);
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
// 在容器中获取需要装配的Bean
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
...
}
if (value != null) {
// 通过反射设置属性值
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
AutowiredMethodElement#inject
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
if (checkPropertySkipping(pvs)) {
return;
}
Method method = (Method) this.member;
Object[] arguments;
if (this.cached) {
// Shortcut for avoiding synchronization...
arguments = resolveCachedArguments(beanName);
}
else {
Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
arguments = new Object[paramTypes.length];
DependencyDescriptor[] descriptors = new DependencyDescriptor[paramTypes.length];
Set<String> autowiredBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(paramTypes.length);
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
for (int i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
MethodParameter methodParam = new MethodParameter(method, i);
DependencyDescriptor currDesc = new DependencyDescriptor(methodParam, this.required);
currDesc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
descriptors[i] = currDesc;
try {
// 在容器中获取需要装配的Bean
Object arg = beanFactory.resolveDependency(currDesc, beanName, autowiredBeans, typeConverter);
if (arg == null && !this.required) {
arguments = null;
break;
}
arguments[i] = arg;
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(methodParam), ex);
}
}
...
}
if (arguments != null) {
try {
// 通过反射调用方法设置元素值
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(method);
method.invoke(bean, arguments);
}
...
}
}
从这里的源码我们可以看出AutowiredFieldElement和AutowiredMethodElement完成自动装配都是先去容器中找对应的Bean,然后通过反射将获取到的Bean设置到目标对象中,来完成Bean的自动装配。
总结
我们可以看出Spring Bean的自动装配过程就是:
- 根据
Class对象,通过反射获取所有的Field和Method信息 - 通反射获取
Field和Method的注解信息,并根据注解类型,判断是否需要自动装配 - 将需要自动装配的元素,封装成
AutowiredFieldElement或AutowiredMethodElement对象 - 调用
AutowiredFieldElement或AutowiredMethodElement的inject方法,唤起后续步骤 - 通过调用容器的
getBean()方法找到需要注入的源数据Bean - 通过反射将找到的源数据Bean注入到目标Bean中
在自动装配过程中还涉及循环依赖的问题,有兴趣的可以看下这篇文章Spring 源码(八)循环依赖
注意:注解注入将在XML注入之前执行;因此,对于通过这两种方法注入的属性,XML注入将覆盖注解注入。













