目录介绍
- 01.先提问一个问题
- 02.EventListener回调原理
- 03.请求开始结束监听
- 04.dns解析开始结束监听
- 05.连接开始结束监听
- 06.TLS连接开始结束监听
- 07.连接绑定和释放监听
- 08.request请求监听
- 09.response响应监听
- 10.如何监听统计耗时
- 11.应用实践之案例
01.先提问一个问题
- OkHttp如何进行各个请求环节的耗时统计呢?
- OkHttp 版本提供了EventListener接口,可以让调用者接收一系列网络请求过程中的事件,例如DNS解析、TSL/SSL连接、Response接收等。
- 通过继承此接口,调用者可以监视整个应用中网络请求次数、流量大小、耗时(比如dns解析时间,请求时间,响应时间等等)情况。
02.EventListener回调原理
先来看一下
public abstract class EventListener { // 按照请求顺序回调 public void callStart(Call call) {} // 域名解析 public void dnsStart(Call call, String domainName) {} public void dnsEnd(Call call, String domainName, List<InetAddress> inetAddressList) {} // 释放当前Transmitter的RealConnection public void connectionReleased(Call call, Connection connection) {} public void connectionAcquired(call, result){}; // 开始连接 public void connectStart(call, route.socketAddress(), proxy){} // 请求 public void requestHeadersStart(@NotNull Call call){} public void requestHeadersEnd(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull Request request) {} // 响应 public void requestBodyStart(@NotNull Call call) {} public void requestBodyEnd(@NotNull Call call, long byteCount) {} // 结束 public void callEnd(Call call) {} // 失败 public void callFailed(Call call, IOException ioe) {} }
03.请求开始结束监听
callStart(Call call) 请求开始
当一个Call(代表一个请求)被同步执行或被添加异步队列中时,即会调用这个回调方法。
需要说明这个方法是在dispatcher.executed/enqueue前执行的。
由于线程或事件流的限制,这里的请求开始并不是真正的去执行的这个请求。如果发生重定向和多域名重试时,这个方法也仅被调用一次。
final class RealCall implements Call { @Override public Response execute() throws IOException { eventListener.callStart(this); client.dispatcher().executed(this); Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain(); if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled"); return result;
} @Override public void enqueue(Callback responseCallback) { eventListener.callStart(this); client.dispatcher().enqueue(new AsyncCall(responseCallback)); } }
callFailed/callEnd 请求异常和请求结束
每一个callStart都对应着一个callFailed或callEnd。
callFailed在两种情况下被调用,第一种是在请求执行的过程中发生异常时。第二种是在请求结束后,关闭输入流时产生异常时。
final class RealCall implements Call { @Override public Response execute() throws IOException { try { client.dispatcher().executed(this); Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain(); if (result == null) throw new IOException("Canceled"); return result; } catch (IOException e) { eventListener.callFailed(this, e); throw e; } } final class AsyncCall extends NamedRunnable { @Override protected void execute() { try { Response response = getResponseWithInterceptorChain(); } catch (IOException e) { eventListener.callFailed(RealCall.this, e); } } } }
//第二种 public final class StreamAllocation { public void streamFinished(boolean noNewStreams, HttpCodec codec, long bytesRead, IOException e) { ... if (e != null) { eventListener.callFailed(call, e); } else if (callEnd) { eventListener.callEnd(call); } ... } }
callEnd也有两种调用场景。第一种也是在关闭流时。第二种是在释放连接时。
public final class StreamAllocation {
public void streamFinished(boolean noNewStreams, HttpCodec codec, long bytesRead, IOException e) { ... if (e != null) { eventListener.callFailed(call, e); } else if (callEnd) { eventListener.callEnd(call); } ... } public void release() { ... if (releasedConnection != null) { eventListener.connectionReleased(call, releasedConnection); eventListener.callEnd(call); } }}
为什么会将关闭流和关闭连接区分开?
- 在http2版本中,一个连接上允许打开多个流,OkHttp使用StreamAllocation来作为流和连接的桥梁。当一个流被关闭时,要检查这条连接上还有没有其他流,如果没有其他流了,则可以将连接关闭了。
- streamFinished和release作用是一样的,都是关闭当前流,并检查是否需要关闭连接。不同的是,当调用者手动取消请求时,调用的是release方法,并由调用者负责关闭请求输出流和响应输入流。
04.dns解析开始结束监听
dnsStart开始
其中的lookup(String hostname)方法代表了域名解析的过程,dnsStart/dnsEnd就是在lookup前后被调用的
DNS解析是请求DNS(Domain Name System)服务器,将域名解析成ip的过程。域名解析工作是由JDK中的InetAddress类完成的。
/** Prepares the socket addresses to attempt for the current proxy or host. */ private void resetNextInetSocketAddress(Proxy proxy) throws IOException { if (proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.SOCKS) { inetSocketAddresses.add(InetSocketAddress.createUnresolved(socketHost, socketPort)); } else { eventListener.dnsStart(call, socketHost); // Try each address for best behavior in mixed IPv4/IPv6 environments. List
addresses = address.dns().lookup(socketHost); if (addresses.isEmpty()) { throw new UnknownHostException(address.dns() + " returned no addresses for " + socketHost); } eventListener.dnsEnd(call, socketHost, addresses); } }
那么RouteSelector这个类是在哪里调用
public final class StreamAllocation { public StreamAllocation(ConnectionPool connectionPool, Address address, Call call, EventListener eventListener, Object callStackTrace) { this.routeSelector = new RouteSelector(address, routeDatabase(), call, eventListener); } }
05.连接开始结束监听
connectStart连接开始
OkHttp是使用Socket接口建立Tcp连接的,所以这里的连接就是指Socket建立一个连接的过程。
当连接被重用时,connectStart/connectEnd不会被调用。当请求被重定向到新的域名后,connectStart/connectEnd会被调用多次。
private void connectSocket(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, Call call, EventListener eventListener) throws IOException { Proxy proxy = route.proxy(); Address address = route.address(); rawSocket = proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.DIRECT || proxy.type() == Proxy.Type.HTTP ? address.socketFactory().createSocket() : new Socket(proxy); eventListener.connectStart(call, route.socketAddress(), proxy); }
connectEnd连接结束
因为创建的连接有两种类型(服务端直连和隧道代理),所以callEnd有两处调用位置。为了在基于代理的连接上使用SSL,需要单独发送CONECT请求。
在连接过程中,无论是Socket连接失败,还是TSL/SSL握手失败,都会回调connectEnd。
public void connect(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout, while (true) { try { establishProtocol(connectionSpecSelector, pingIntervalMillis, call, eventListener); eventListener.connectEnd(call, route.socketAddress(), route.proxy(), protocol); break; } catch (IOException e) { eventListener.connectFailed(call, route.socketAddress(), route.proxy(), null, e); } }
private void connectTunnel(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout, Call call, EventListener eventListener) throws IOException { Request tunnelRequest = createTunnelRequest(); HttpUrl url = tunnelRequest.url(); for (int i = 0; i < MAX_TUNNEL_ATTEMPTS; i++) { connectSocket(connectTimeout, readTimeout, call, eventListener); eventListener.connectEnd(call, route.socketAddress(), route.proxy(), null); } }
06.TLS连接开始结束监听
开始连接,代码如下所示
在上面看到,在Socket建立连接后,会执行一个establishProtocol方法,这个方法的作用就是TSL/SSL握手。
当存在重定向或连接重试的情况下,secureConnectStart/secureConnectEnd会被调用多次。
private void establishProtocol(ConnectionSpecSelector connectionSpecSelector, int pingIntervalMillis, Call call, EventListener eventListener) throws IOException { if (route.address().sslSocketFactory() == null) { protocol = Protocol.HTTP_1_1; socket = rawSocket; return; } eventListener.secureConnectStart(call); connectTls(connectionSpecSelector); eventListener.secureConnectEnd(call, handshake); }
结合连接监听可知
- 如果我们使用了HTTPS安全连接,在TCP连接成功后需要进行TLS安全协议通信,等TLS通讯结束后才能算是整个连接过程的结束,也就是说connectEnd在secureConnectEnd之后调用。
所以顺序是这样的
- connectStart ---> secureConnectStart ---> secureConnectEnd ---> ConnectEnd
07.连接绑定和释放监听
因为OkHttp是基于连接复用的,当一次请求结束后并不会马上关闭当前连接,而是放到连接池中。
当有相同域名的请求时,会从连接池中取出对应的连接使用,减少了连接的频繁创建和销毁。
当根据一个请求从连接池取连接时,并打开输入输出流就是acquired,用完释放流就是released。
如果直接复用StreamAllocation中的连接,则不会调用connectionAcquired/connectReleased。
private RealConnection findConnection(int connectTimeout, int readTimeout, int writeTimeout, int pingIntervalMillis, boolean connectionRetryEnabled) throws IOException { synchronized (connectionPool) { if (result == null) { // 第一次查缓存 Attempt to get a connection from the pool. // Attempt to get a connection from the pool. Internal.instance.get(connectionPool, address, this, null); } } if (releasedConnection != null) { eventListener.connectionReleased(call, releasedConnection); } if (foundPooledConnection) { eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result); } synchronized (connectionPool) { if (canceled) throw new IOException("Canceled"); if (newRouteSelection) { //第二次查缓存 List
routes = routeSelection.getAll(); for (int i = 0, size = routes.size(); i < size; i++) { Route route = routes.get(i); Internal.instance.get(connectionPool, address, this, route); if (connection != null) { foundPooledConnection = true; result = connection; this.route = route; break; } } } if (!foundPooledConnection) { //如果缓存没有,则新建连接 route = selectedRoute; refusedStreamCount = 0; result = new RealConnection(connectionPool, selectedRoute); acquire(result, false); } } // If we found a pooled connection on the 2nd time around, we're done. if (foundPooledConnection) { eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result); return result; } // Do TCP + TLS handshakes. This is a blocking operation. result.connect(connectTimeout, readTimeout, writeTimeout, pingIntervalMillis, connectionRetryEnabled, call, eventListener); routeDatabase().connected(result.route()); eventListener.connectionAcquired(call, result); return result; }
connectionAcquired是在连接成功后被调用的。
- 但是在连接复用的情况下没有连接步骤,connectAcquired会在获取缓存连接后被调用。由于StreamAllocation是连接“Stream”和“Connection”的桥梁,所以在StreamAllocation中会持有一个RealConnection引用。StreamAllocation在查找可用连接的顺序为:StreamAllocation.RealConnection -> ConnectionPool -> ConnectionPool -> new RealConnection
08.request请求监听
在OkHttp中,HttpCodec负责对请求和响应按照Http协议进行编解码,包含发送请求头、发送请求体、读取响应头、读取响应体。
requestHeaders开始和结束,这个直接看CallServerInterceptor拦截器代码即可。
public final class CallServerInterceptor implements Interceptor { @Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException { RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain; HttpCodec httpCodec = realChain.httpStream(); StreamAllocation streamAllocation = realChain.streamAllocation(); RealConnection connection = (RealConnection) realChain.connection(); Request request = realChain.request(); long sentRequestMillis = System.currentTimeMillis(); realChain.eventListener().requestHeadersStart(realChain.call()); httpCodec.writeRequestHeaders(request); realChain.eventListener().requestHeadersEnd(realChain.call(), request); if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method()) && request.body() != null) { if (responseBuilder == null) { // Write the request body if the "Expect: 100-continue" expectation was met. realChain.eventListener().requestBodyStart(realChain.call()); long contentLength = request.body().contentLength(); CountingSink requestBodyOut = new CountingSink(httpCodec.createRequestBody(request, contentLength)); BufferedSink bufferedRequestBody = Okio.buffer(requestBodyOut); request.body().writeTo(bufferedRequestBody); bufferedRequestBody.close(); realChain.eventListener().requestBodyEnd(realChain.call(), requestBodyOut.successfulCount); } } return response; } }
09.response响应监听
responseHeadersStart和responseHeadersEnd代码如下所示
public final class CallServerInterceptor implements Interceptor { @Override public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException { Response.Builder responseBuilder = null; if (HttpMethod.permitsRequestBody(request.method()) && request.body() != null) { if ("100-continue".equalsIgnoreCase(request.header("Expect"))) { httpCodec.flushRequest(); realChain.eventListener().responseHeadersStart(realChain.call()); responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(true); } } httpCodec.finishRequest(); if (responseBuilder == null) { realChain.eventListener().responseHeadersStart(realChain.call()); responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(false); } int code = response.code(); if (code == 100) { // server sent a 100-continue even though we did not request one. // try again to read the actual response responseBuilder = httpCodec.readResponseHeaders(false); response = responseBuilder .request(request) .handshake(streamAllocation.connection().handshake()) .sentRequestAtMillis(sentRequestMillis) .receivedResponseAtMillis(System.currentTimeMillis()) .build(); code = response.code(); } realChain.eventListener() .responseHeadersEnd(realChain.call(), response); return response; } }responseBodyStart监听
响应体的读取有些复杂,要根据不同类型的Content-Type决定如何读取响应体,例如固定长度的、基于块(chunk)数据的、未知长度的。具体看openResponseBody方法里面的代码。
同时Http1与Http2也有不同的解析方式。下面以Http1为例。
public final class Http1Codec implements HttpCodec {
@Override public ResponseBody openResponseBody(Response response) throws IOException { streamAllocation.eventListener.responseBodyStart(streamAllocation.call); String contentType = response.header("Content-Type"); if (!HttpHeaders.hasBody(response)) { Source source = newFixedLengthSource(0); return new RealResponseBody(contentType, 0, Okio.buffer(source)); } if ("chunked".equalsIgnoreCase(response.header("Transfer-Encoding"))) { Source source = newChunkedSource(response.request().url()); return new RealResponseBody(contentType, -1L, Okio.buffer(source)); } long contentLength = HttpHeaders.contentLength(response); if (contentLength != -1) { Source source = newFixedLengthSource(contentLength); return new RealResponseBody(contentType, contentLength, Okio.buffer(source)); } return new RealResponseBody(contentType, -1L, Okio.buffer(newUnknownLengthSource())); } }
responseBodyEnd监听
由下面代码可知,当响应结束后,会调用连接callEnd回调(如果异常则会调用callFailed回调)
public final class StreamAllocation { public void streamFinished(boolean noNewStreams, HttpCodec codec, long bytesRead, IOException e) { eventListener.responseBodyEnd(call, bytesRead); if (releasedConnection != null) { eventListener.connectionReleased(call, releasedConnection); } if (e != null) { eventListener.callFailed(call, e); } else if (callEnd) { eventListener.callEnd(call); } } }
10.如何监听统计耗时
如何消耗记录时间
- 在OkHttp库中有一个EventListener类。该类是网络事件的侦听器。扩展这个类以监视应用程序的HTTP调用的数量、大小和持续时间。
- 所有启动/连接/获取事件最终将接收到匹配的结束/释放事件,要么成功(非空参数),要么失败(非空可抛出)。
- 比如,可以在开始链接记录时间;dns开始,结束等方法解析记录时间,可以计算dns的解析时间。
- 比如,可以在开始请求记录时间,记录connectStart,connectEnd等方法时间,则可以计算出connect连接时间。
代码如下所示
Eventlistener只适用于没有并发的情况,如果有多个请求并发执行我们需要使用Eventlistener. Factory来给每个请求创建一个Eventlistener。
这个mRequestId是唯一值,可以选择使用AtomicInteger自增+1的方式设置id,这个使用了cas保证多线程条件下的原子性特性。
/**
@author yangchongemail : yangchong211@163.comtime : 2019/07/22desc : EventListener子类revise:
*/ public class NetworkListener extends EventListener {
private static final String TAG = "NetworkEventListener"; private static AtomicInteger mNextRequestId = new AtomicInteger(0); private String mRequestId ; public static Factory get(){ Factory factory = new Factory() { @NotNull @Override public EventListener create(@NotNull Call call) { return new NetworkListener(); } }; return factory; } @Override public void callStart(@NotNull Call call) { super.callStart(call); //mRequestId = mNextRequestId.getAndIncrement() + ""; //getAndAdd,在多线程下使用cas保证原子性 mRequestId = String.valueOf(mNextRequestId.getAndIncrement()); ToolLogUtils.i(TAG+"-------callStart---requestId-----"+mRequestId); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.CALL_START); saveUrl(call.request().url().toString()); } @Override public void dnsStart(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull String domainName) { super.dnsStart(call, domainName); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "dnsStart"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.DNS_START); } @Override public void dnsEnd(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull String domainName, @NotNull List<InetAddress> inetAddressList) { super.dnsEnd(call, domainName, inetAddressList); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "dnsEnd"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.DNS_END); } @Override public void connectStart(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress, @NotNull Proxy proxy) { super.connectStart(call, inetSocketAddress, proxy); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "connectStart"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.CONNECT_START); } @Override public void secureConnectStart(@NotNull Call call) { super.secureConnectStart(call); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "secureConnectStart"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.SECURE_CONNECT_START); } @Override public void secureConnectEnd(@NotNull Call call, @Nullable Handshake handshake) { super.secureConnectEnd(call, handshake); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "secureConnectEnd"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.SECURE_CONNECT_END); } @Override public void connectEnd(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress, @NotNull Proxy proxy, @Nullable Protocol protocol) { super.connectEnd(call, inetSocketAddress, proxy, protocol); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "connectEnd"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.CONNECT_END); } @Override public void connectFailed(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull InetSocketAddress inetSocketAddress, @NotNull Proxy proxy, @Nullable Protocol protocol, @NotNull IOException ioe) { super.connectFailed(call, inetSocketAddress, proxy, protocol, ioe); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "connectFailed"); } @Override public void requestHeadersStart(@NotNull Call call) { super.requestHeadersStart(call); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "requestHeadersStart"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.REQUEST_HEADERS_START); } @Override public void requestHeadersEnd(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull Request request) { super.requestHeadersEnd(call, request); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "requestHeadersEnd"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.REQUEST_HEADERS_END); } @Override public void requestBodyStart(@NotNull Call call) { super.requestBodyStart(call); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "requestBodyStart"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.REQUEST_BODY_START); } @Override public void requestBodyEnd(@NotNull Call call, long byteCount) { super.requestBodyEnd(call, byteCount); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "requestBodyEnd"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.REQUEST_BODY_END); } @Override public void responseHeadersStart(@NotNull Call call) { super.responseHeadersStart(call); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "responseHeadersStart"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.RESPONSE_HEADERS_START); } @Override public void responseHeadersEnd(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull Response response) { super.responseHeadersEnd(call, response); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "responseHeadersEnd"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.RESPONSE_HEADERS_END); } @Override public void responseBodyStart(@NotNull Call call) { super.responseBodyStart(call); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "responseBodyStart"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.RESPONSE_BODY_START); } @Override public void responseBodyEnd(@NotNull Call call, long byteCount) { super.responseBodyEnd(call, byteCount); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "responseBodyEnd"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.RESPONSE_BODY_END); } @Override public void callEnd(@NotNull Call call) { super.callEnd(call); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "callEnd"); saveEvent(NetworkTraceBean.CALL_END); generateTraceData(); NetWorkUtils.timeoutChecker(mRequestId); } @Override public void callFailed(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull IOException ioe) { super.callFailed(call, ioe); ToolLogUtils.d(TAG, "callFailed"); } private void generateTraceData(){ NetworkTraceBean traceModel = IDataPoolHandleImpl.getInstance().getNetworkTraceModel(mRequestId); Map<String, Long> eventsTimeMap = traceModel.getNetworkEventsMap(); Map<String, Long> traceList = traceModel.getTraceItemList(); traceList.put(NetworkTraceBean.TRACE_NAME_TOTAL,NetWorkUtils.getEventCostTime(eventsTimeMap,NetworkTraceBean.CALL_START, NetworkTraceBean.CALL_END)); traceList.put(NetworkTraceBean.TRACE_NAME_DNS,NetWorkUtils.getEventCostTime(eventsTimeMap,NetworkTraceBean.DNS_START, NetworkTraceBean.DNS_END)); traceList.put(NetworkTraceBean.TRACE_NAME_SECURE_CONNECT,NetWorkUtils.getEventCostTime(eventsTimeMap,NetworkTraceBean.SECURE_CONNECT_START, NetworkTraceBean.SECURE_CONNECT_END)); traceList.put(NetworkTraceBean.TRACE_NAME_CONNECT,NetWorkUtils.getEventCostTime(eventsTimeMap,NetworkTraceBean.CONNECT_START, NetworkTraceBean.CONNECT_END)); traceList.put(NetworkTraceBean.TRACE_NAME_REQUEST_HEADERS,NetWorkUtils.getEventCostTime(eventsTimeMap,NetworkTraceBean.REQUEST_HEADERS_START, NetworkTraceBean.REQUEST_HEADERS_END)); traceList.put(NetworkTraceBean.TRACE_NAME_REQUEST_BODY,NetWorkUtils.getEventCostTime(eventsTimeMap,NetworkTraceBean.REQUEST_BODY_START, NetworkTraceBean.REQUEST_BODY_END)); traceList.put(NetworkTraceBean.TRACE_NAME_RESPONSE_HEADERS,NetWorkUtils.getEventCostTime(eventsTimeMap,NetworkTraceBean.RESPONSE_HEADERS_START, NetworkTraceBean.RESPONSE_HEADERS_END)); traceList.put(NetworkTraceBean.TRACE_NAME_RESPONSE_BODY,NetWorkUtils.getEventCostTime(eventsTimeMap,NetworkTraceBean.RESPONSE_BODY_START, NetworkTraceBean.RESPONSE_BODY_END)); } private void saveEvent(String eventName){ NetworkTraceBean networkTraceModel = IDataPoolHandleImpl.getInstance().getNetworkTraceModel(mRequestId); Map<String, Long> networkEventsMap = networkTraceModel.getNetworkEventsMap(); networkEventsMap.put(eventName, SystemClock.elapsedRealtime()); } private void saveUrl(String url){ NetworkTraceBean networkTraceModel = IDataPoolHandleImpl.getInstance().getNetworkTraceModel(mRequestId); networkTraceModel.setUrl(url); }}
关于执行顺序,打印结果如下所示
2020-09-22 20:50:15.351 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: dnsStart 2020-09-22 20:50:15.373 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: dnsEnd 2020-09-22 20:50:15.374 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: connectStart 2020-09-22 20:50:15.404 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: secureConnectStart 2020-09-22 20:50:15.490 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: secureConnectEnd 2020-09-22 20:50:15.490 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: connectEnd 2020-09-22 20:50:15.492 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: requestHeadersStart 2020-09-22 20:50:15.492 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: requestHeadersEnd 2020-09-22 20:50:15.528 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: responseHeadersStart 2020-09-22 20:50:15.528 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: responseHeadersEnd 2020-09-22 20:50:15.532 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: responseBodyStart 2020-09-22 20:50:15.534 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: responseBodyEnd 2020-09-22 20:50:15.547 28144-28277/cn.com.zwwl.bayuwen D/NetworkEventListener: callEnd
11.应用实践之案例

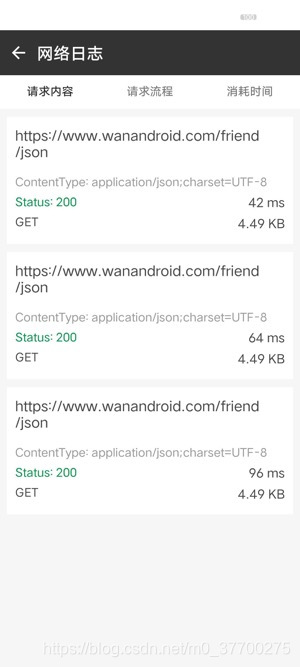



- 网络拦截分析,主要是分析网络流量损耗,以及request,respond过程时间。打造网络分析工具……
- 项目代码地址:https://github.com/yangchong211/YCAndroidTool
- 如果你觉得这个拦截网络助手方便了测试,以及开发中查看网络数据,可以star一下……






