前言
The master has failed more times than the beginner has tried.
编程的学习,大师失败的次数比初学者尝试的次数要多得多。
编写测试程序
源码文件以 _test 结尾:xxx_test.go
测试方法以 Test 开头:func TestXXX(t *testing.T) {...}
注意:在 Go 语言中,大写的方法名代表包外可以访问,对于测试来说没有意义。
示例代码:
package try_test
import "testing"
// 函数方法以大写 Test 开头,参数列表里固定为 t *testing.T,具体是啥之后说
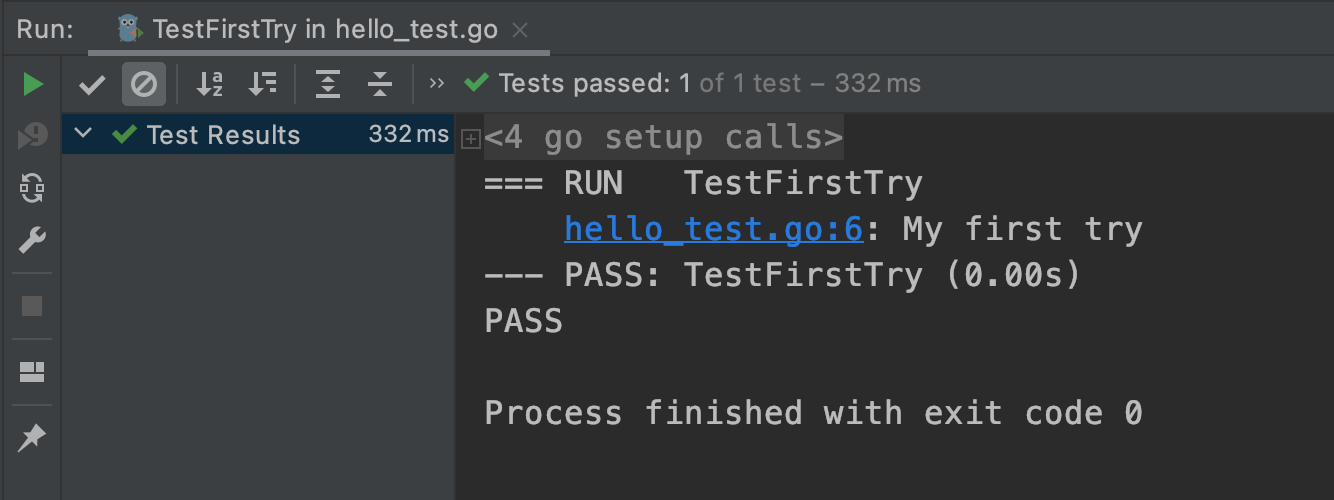
func TestFirstTry(t *testing.T) {
t.Log("My first try")
}运行结果:
在接下来的内容中,我们会大量使用单元测试进行试错,更好的理解知识点。
实现 Fibonacci 数列
package Fibnoacci
import (
"testing"
)
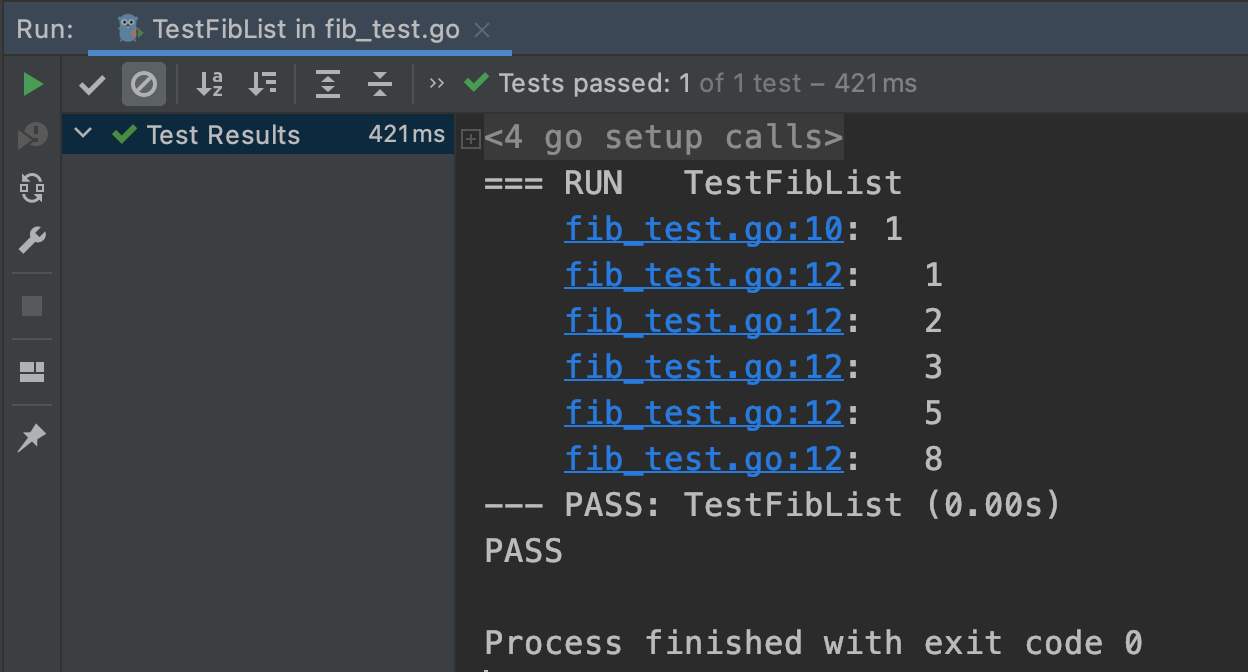
func TestFibList(t *testing.T) {
// Go 语言的赋值方式,:= 是声明并赋值,并且系统自动推断类型,不需要 var 关键字
a := 1
b := 1
t.Log(a)
for i := 0; i < 5; i++ {
t.Log(" ", b)
tmp := a
a = b
b = tmp + a
}
}
输出结果:
变量赋值
与其他主要编程语言的差异
赋值可以进行自动类型推断
在一个赋值语句中可以对多个变量进行同时赋值
func TestExchange(t *testing.T) { a := 1 b := 2 //tmp := a //a = b //b = tmp a, b = b, a t.Log(a, b) }Go 语言支持通过一行代码
a, b = b, a直接交换两个变量的值。
常量定义
与其他主要编程语言的差异
支持快速设置连续的值
通过例子说明一下
package constan_test
import "testing"
// 自增的方式,Monday=1,Tuesday=2,Wednesday=3
const (
Monday = iota + 1
Tuesday
Wednesday
)
// 移位的方式,Readable=1,Writeable=2,Executable=4
const (
Readable = 1 << iota
Writeable
Executable
)
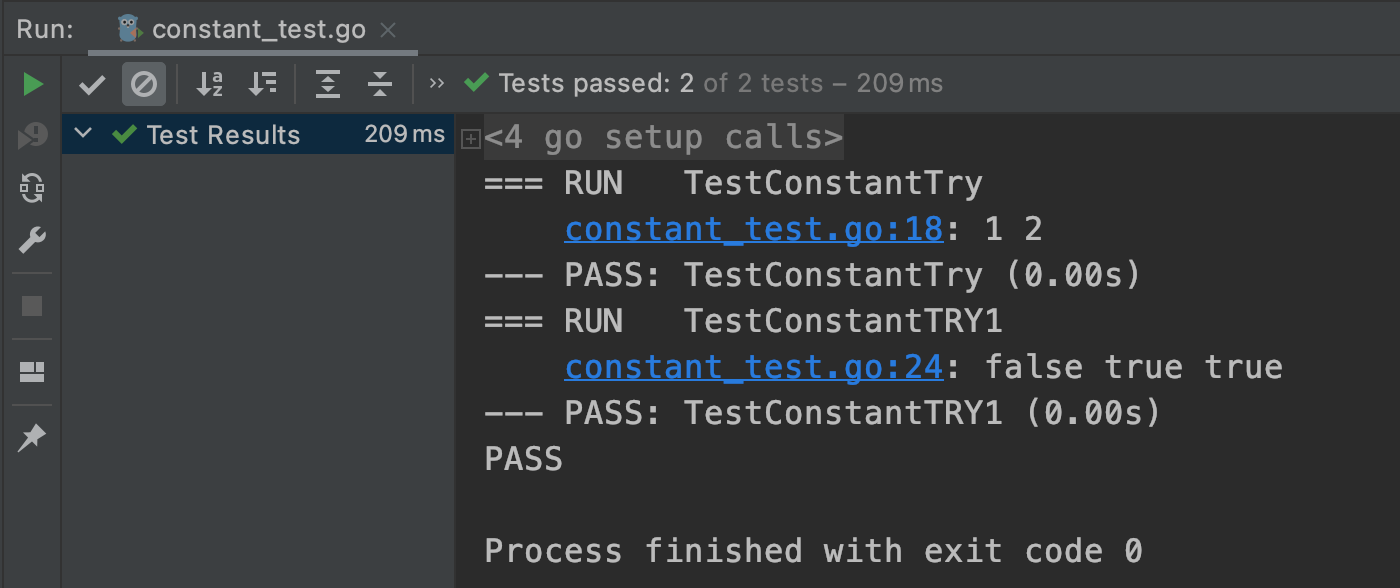
func TestConstantTry(t *testing.T) {
t.Log(Monday, Tuesday)
}
func TestConstantTRY1(t *testing.T) {
// 6 -> 0110
a := 6
// 0110 & 0001 -> 得到0,因此返回false;0110 & 0010 -> 得到2,因此返回true;...
t.Log(a&Readable == Readable, a&Writeable == Writeable, a&Executable == Executable)
}
测试结果: