服务端基础概念
网站的组成
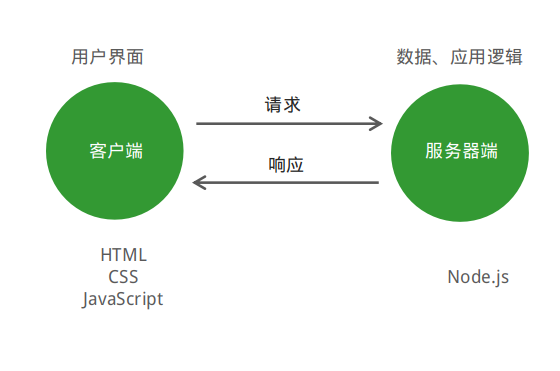
网站应用程序主要分为两大部分:客户端和服务器端。
客户端:在浏览器中运行的部分,就是用户看到并与之交互的界面程 序。使用HTML、CSS、JavaScript构建。
服务器端:在服务器中运行的部分,负责存储数据和处理应用逻辑。
网站服务器
能够提供网站访问服务的机器便叫做网站服务器,它能够接受客户端的请求,也能够做出对客户端做出响应
IP地址
互联网中的唯一标示
域名
由于IP地址难于记忆,所以产生了域名的概念,所谓域名就是平时上网所使用的网址。
http://www.itheima.com => http://124.165.219.100/
虽然在地址栏中输入的是网址, 但是最终还是会将域名转换为ip才能访问到指定的网站服务器。
使用方法
- nslookup+空格+网址 查询网站的IP地址
- ping+空格+网址,并点击回车
端口
端口是计算机与外界通讯交流的出口,用来提供不同的服务。
为什么要学习node.js
- 能够和后端程序员更加紧密的配合
- 能够扩宽自己的知识视野
- 学习前端知识需要后端知识的支撑(ajax)
node开发需要做的事情
- 实现网站的业务逻辑
- 实现数据的增删改查
为什么选择node
- 使用javascript语法开发后端应用
- 一些公司要求前端工程师必须要掌握node开发
- 生态系统活跃,有大量开源库可以使用
- 前端开发工具大多都是基于node开发
为什么要使用node开发呢
node是基于chrome v8引擎的javascript代码运行环境
windows及liux安装node.js的方法。
- windows安装node.js的方法:https://www.cnblogs.com/liuqi...
- liux安装node.js的方法:https://segmentfault.com/a/11...
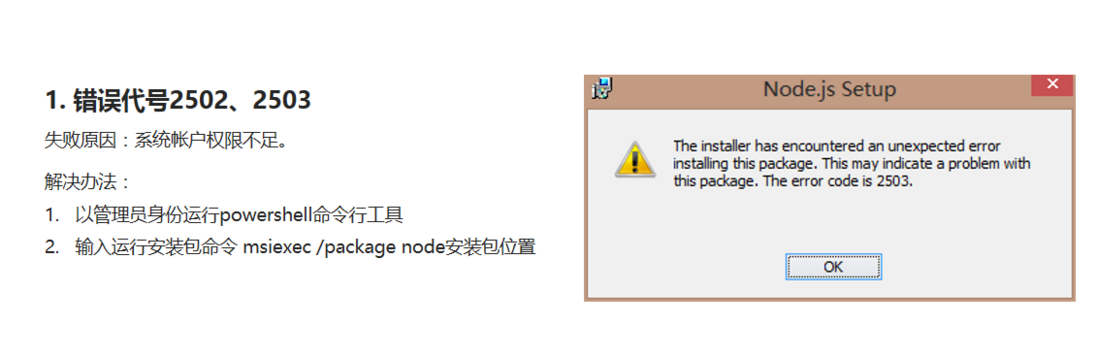
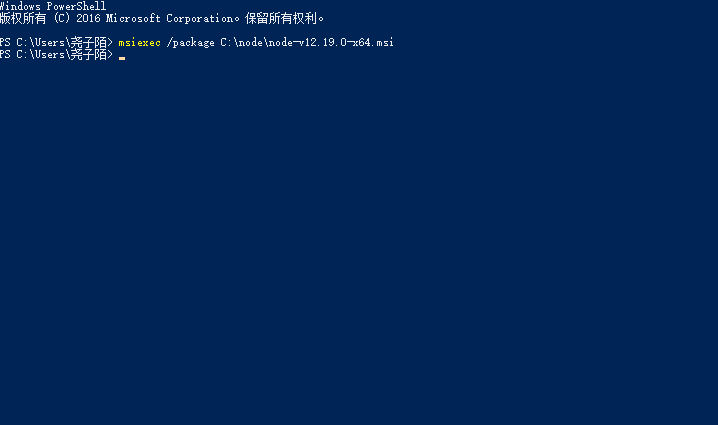
node安装失败的解决方法
系统权限不足
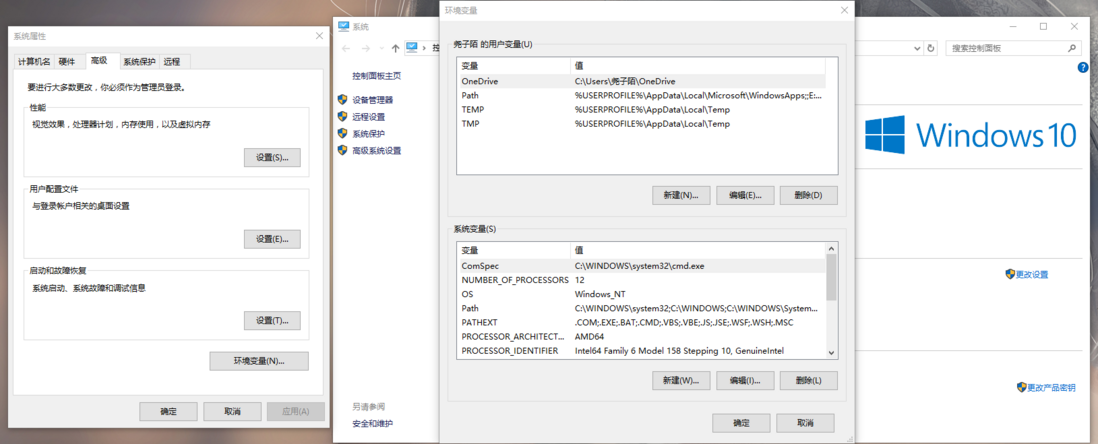
PATH环境变量
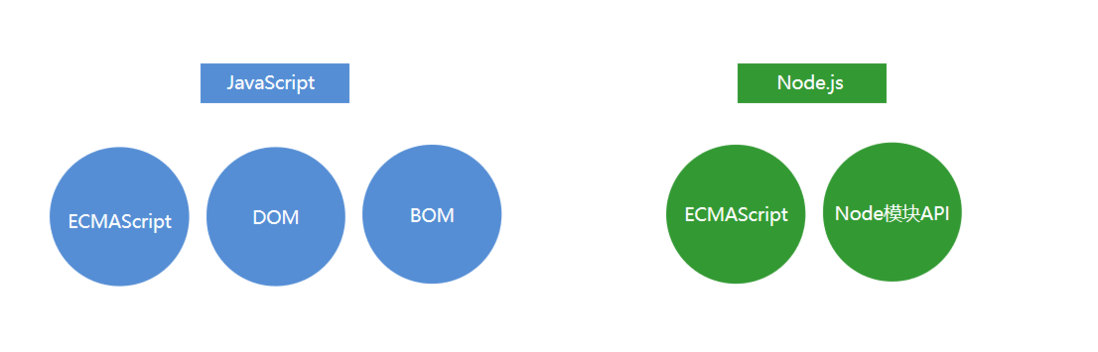
Node.js的组成
Node如何执行js文件
- cd:跳转目录
cd ../:跳转上一级目录
- clear:清除命令行
Node打开js文件
点击键盘上的shift键,再次点击鼠标,打开命令行工具,即可打开js文件
function fn() {
console.log('hello Node');
}
fn();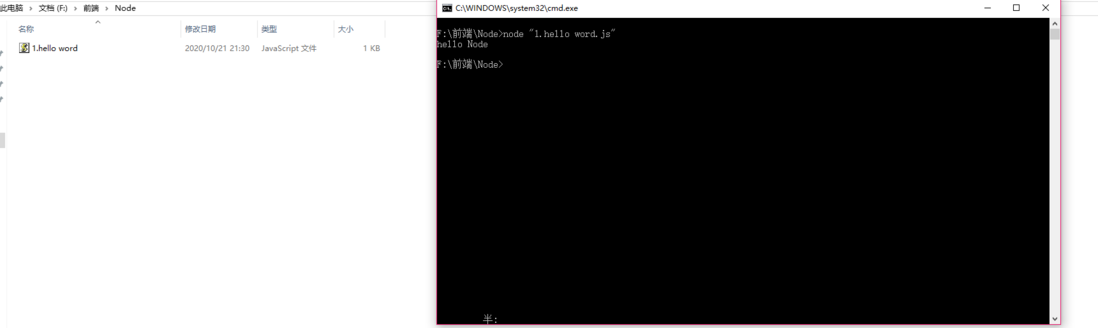
global
浏览器全局对象是window Node.js全局对象是global

global.console.log('hello Node.js');
global.setTimeout(() => {
console.log('hello Node');
}, 2000);
node模块化开发
js在使用的时候存在两大问题:文件依赖及命名冲突,而Node模块化开发恰恰解决这个问题,文件之间处于半封闭的状态,把需要的模块暴露出来,不需要的模块则不需要暴露出来
软件中的模块化开发
一个功能就是一个模块,多个模块组成一个完整的应用,抽取一个模块不会影响其它模块的运行
模块开发的第一种方法
a模块
const add = (n1, n2) => n1 + n2;
// 导出a模块
exports.add = add;b模块
// 导入a模块
const b = require('./a');
// 使用a模块的方法
console.log(b.add(20, 50));
模块成员的第二种方法
使用module.exports导出模块
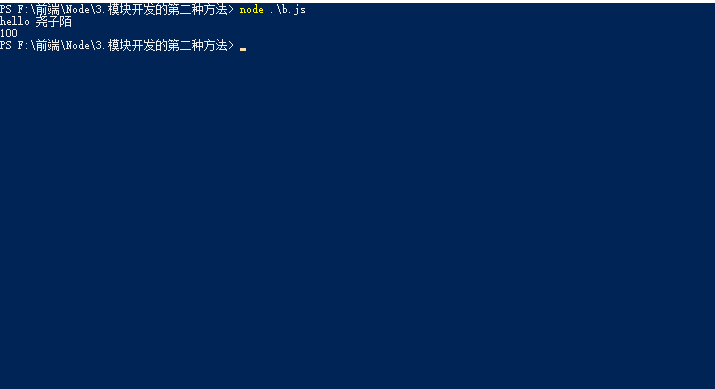
a模块
const Name = name => `hello ${name}`;
module.exports.Name = Name;
const x = 100;
// 导出模块
exports.x = x;b模块
let b = require('./a');
console.log(b.Name('尧子陌'));
console.log(b.x)
module.exports与exports的区别
当module.exports与exports指向不同的地址时,最后的结果以module.exports为准a模块
module.exports = {
name: "尧子陌"
},
exports = {
name: "张三"
}
b模块
let b = require('./a.js');
console.log(b);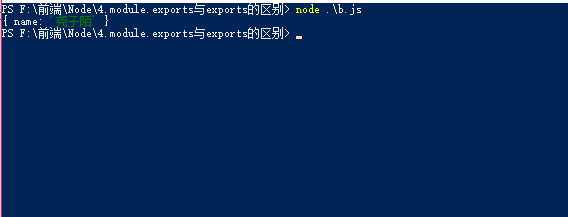
Node系统模块
Node运行环境提供的API,便叫做系统模块
fs系统
f:文件 s:系统 fs:文件系统读取文件
- readFile:读取文件
- err:如果文件读取出错,err是一个对象,包含错误信息,如果文件读取正确,err的值为null
- doc:是文件读取的结果

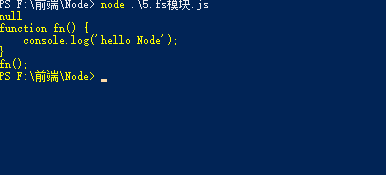
let fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile('./1.hello word.js', 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
console.log(err);
console.log(doc);
})
写入文件

写入文件后,会自动生成demo.text,内容为尧子陌
let fs = require('fs');
fs.writeFile('./demo.text', '尧子陌', err => {
if (err != null) {
console.log(err);
return;
}
console.log('文件写入成功');
})
path模块
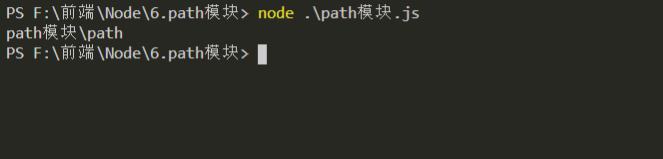
path模块中join()方法可以判断我们使用的是哪种操作系统,从而可以实现符合当前的操作系统的路径拼接

// 引入path模块
let path = require('path');
// 开始拼接路径
let pathFile = path.join('path模块', 'path');
console.log(pathFile);
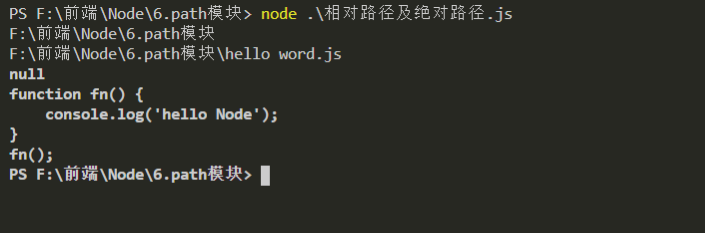
系统模块中的相对路径和绝对路径
大多数的情况下,相对路径是相对于命令行所在的目录,而绝对路径是相对于当前的工作目录
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path')
console.log(__dirname);
console.log(path.join(__dirname, 'hello word.js'));
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname, 'hello word.js'), 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
console.log(err);
console.log(doc);
})
第三方模块
别人写好的 具有特定的功能,我们可以直接使用的模块被称为第三方模块
第三方模块的存在形式
- js文件形式存在,主要提供API为主
- 命令行形式存在,辅助项目开发
npm
npm:node的第三方模块管理工具
使用方法
- 下载模块:npm install 模块名称
- 卸载模块:npm uninstall package 模块名称
nodemon
nodemon:命令行工具,用来辅助项目开发,主要用来监视用户状态,简单而言,就是代码发生改变时,命令行的结果同步改变
下载方式:npm install nodemon -g
nrm
nrm:npm下载切换工具
使用方法
1.使用npm install nrm –g 下载它
2.查询可用下载地址列表 nrm ls
3.切换npm下载地址 nrm use 下载地址名称
## Node.js的模块加载机制
当模块名没有后缀时
require('./find.js)
require('./find')
1.如果模块后缀省略,先找同名JS文件再找同名JS文件夹
2.require方法根据模块路径查找模块,如果是完整路径,直接引入模块。
3.如果找到了同名文件夹,找文件夹中的index.js
4.如果文件夹中没有index.js就会去当前文件夹中的package.json文件中查找main选项中的入口文件
5.如果找指定的入口文件不存在或者没有指定入口文件就会报错,模块没有被找到
当模块名既没有后缀也没有路径时
require('find)
1.Node.js会假设它是系统模块
2.Node.js会去node_modules文件夹中
3.首先看是否有该名字的JS文件
4.再看是否有该名字的文件夹
5.如果是文件夹看里面是否有index.js
6.如果没有index.js查看该文件夹中的package.json中的main选项确定模块入口文件
7.否则找不到报错
URL
URL:统一资源定位符,也就是我们常说的网页地址
URL的组成
传输协议://服务器IP或域名:端口/资源所在位置标识
http://www.itcast.cn/news/20181018/09152238514.html
http:超文本传输协议,提供了一种发布和接收HTML页面的方法。
开发过程中客户端和服务端的说明
在开发的过程中,客户端和服务端使用的是同一台电脑,即为开发人员电脑

创建自己的服务器
- req:请求
- res:响应
//引进http模块
const http = require('http');
//创建服务器对象app
const app = http.createServer();
//当有服务器请求的时候,便会启动服务器
app.on('request', (req, res) => {
// 设置页面内容是html,编码格式是utf-8。
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8' });
//返回服务器响应的内容
res.end("尧子陌")
})
//监听端口
app.listen(8080);
//附加说明
console.log('服务器启动成功');

请求报文
请求方式
- GET:请求数据
- POST:发送数据
请求地址

//引进http模块
const http = require('http');
//创建服务器对象app
const app = http.createServer();
//当有服务器请求的时候,便会启动服务器
app.on('request', (req, res) => {
// 设置页面内容是html,编码格式是utf-8。
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': 'text/html; charset=utf-8' });
//获取请求报文的属性
console.log(req.headers['accept']);
//根据请求的网址响应不同的内容
if (req.url == '/index' || req.url == '/') {
res.end("welcome to home")
} else if (req.url = '/list') {
res.end("welcome to list")
} else {
res.end('not found')
}
//根据请求方式响应不同的内容
if (req.method == 'GET') {
res.end('get')
} else if (req.method == 'POST') {
res.end('post')
}
})
//监听端口
app.listen(8080);
//附加说明
console.log('服务器启动成功');响应报文
HTTP状态吗
- 200:请求成功
- 404:请求的资源没有被找到
- 500:服务器端错误
- 400:客户端请求有语法错误
内容类型
- text/html
- text/css
- application/javascript
- image/jpeg
- application/json
HTTP请求与响应处理
客户端向服务器端发送请求时,有时需要携带一些客户信息,客户信息需要通过请求参数的形式传递到服务器端,比如登录操作。
GET请求参数
参数被放置在浏览器地址栏中,例如:http://localhost:3000/?name=zhangsan&age=20
参数获取需要借助系统模块url,url模块用来处理url地址
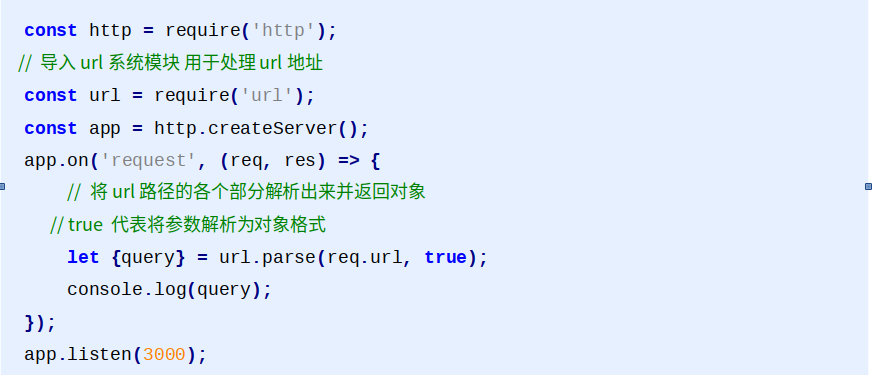
POST请求参数
说明
- 参数是放在请求体中进行传输
- 获取post请求参数需要data和end事件
- 需要querystring来将请求参数转换成对象格式

node路由
http://localhost:3000/index
http://localhost:3000/login
简单来说:请求内容响应相对应的内容
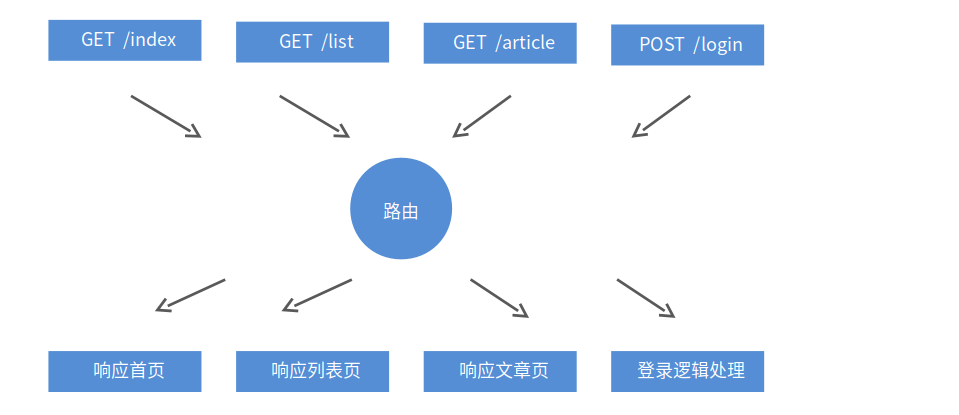
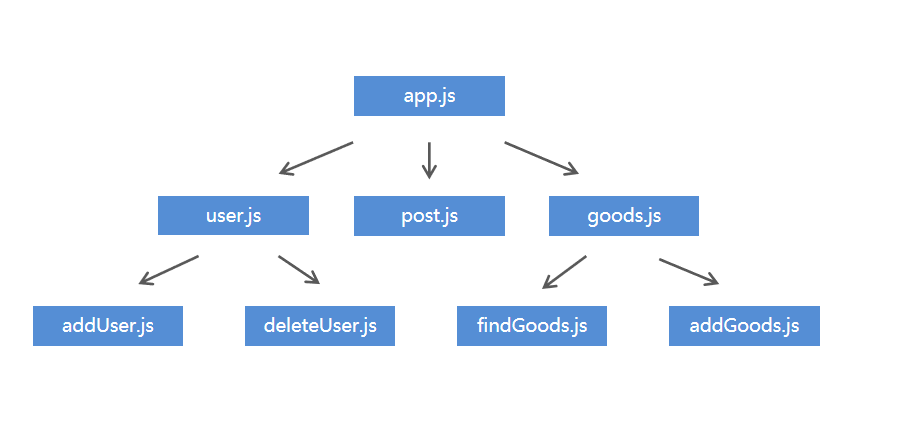
app.js
//引进系统模块
const http = require("http");
//引进url系统模块
const url = require('url');
//创建网站服务器对象
let app = http.createServer();
//当有请求发送进来时
app.on('request', (req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
'content-type': 'text/html;charset=utf8'
});
console.log(req.url);
console.log(url.parse(req.url, true));
//获取请求方式
let method = req.method.toLowerCase();
//获取请求地址
let { query, pathname } = url.parse(req.url, true);
//get请求及post请求
if (method == 'get') {
//get请求
if (pathname == '/' || pathname == '/index') {
res.end('<h1>欢迎来到主页</h1>')
} else if (pathname == '/list') {
res.end("<h1>欢迎来到列表页</h1>")
} else {
res.end('404')
}
} else if (method == 'post') {
if (pathname == '/main') {
res.end('<h1>欢迎来到主目录</h1>')
} else if (pathname == '/detail') {
res.end('<h1>欢迎来到详情页</h1>')
} else {
res.end('404')
}
}
})
//设置监听端口
app.listen(8080);
console.log('服务器启动成功');
form.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>form</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- method:当前表单提交的方式
action:当前表单提交的地址 -->
<form method="post" action="http://localhost:8080/main">
<input type="text" name="username" id="">
<input type="password" name="password" id="">
<input type="submit" value="提交">
</form>
</body>
</html>
node资源
静态资源
服务器端不需要处理,可以直接响应给客户端的资源就是静态资源,例如CSS、JavaScript、image文件。
动态资源
相同的请求地址不同的响应资源,这种资源就是动态资源。
//引进http模块
const http = require('http');
//引进url模块
const url = require('url')
//引进path模块
const path = require('path')
//引进fs模块
const fs = require('fs')
//引进mime模块
const mime = require('mime');
//创建服务器对象
const app = http.createServer();
//当向服务器发送请求的时候
app.on('request', (req, res) => {
res.writeHead(200, {
'content-type': 'text/html;charset=utf8'
});
//获取用户的请求路径
let pathname = url.parse(req.url).pathname;
pathname = pathname == '/' ? '/index.html' : pathname
let realpath = path.join(__dirname, 'public' + pathname)
//获取当前文件内的数据类型
let type = mime.getType(realpath);
console.log(type);
//读取文件
fs.readFile(realpath, 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
//如果文件读取失败
if (err != null) {
res.writeHead(200, {
'content-type': 'text/html;charset=utf8'
});
res.end('文件读取失败');
return;
}
res.writeHead(200, {
'content-type': type
});
res.end(doc)
})
});
//设置服务器端口
app.listen(3000)
console.log('服务器启动成功');
客户端请求路径
GET方式
- 浏览器地址栏
- link标签的href属性
- script标签的src属性
- img标签的src属性
- Form表单提交
POST方式
- From:表单提交
Node.js异步编程
同步API
同步API:只有当前API执行完毕后,才会执行下一个API
console.log('before');
console.log('after');异步API
异步API: 当前API的执行不会影响后续代码的执行
console.log('before');
setTimeout(
() => {
console.log('last');
}, 2000
)
console.log('after');
同步API,异步API的区别(获取返回值)
同步API可以从返回值中拿到API执行的结果,而异步API是不可以的
同步API
function sum(num1, num2) {
return num1 + num2;
}
const result = sum(20, 50);
console.log(result);
异步API
function getMsg() {
setTimeout(() => {
return {
msg: "hello WORD"
}
}, 2000);
};
console.log(getMsg());
Node中的回调函数
回调函数
回调函数可以作为另一个函数的参数使用,这种函数便叫做回调函数
function getMsg(callback) {
callback('2020')
};
getMsg(function(n) {
console.log('callback执行成功');
console.log(n);
})
回调函数可让异步API返回API的执行结果
function getMsg(callback) {
setTimeout(() => {
callback({
msg: "hello word"
})
}, 2000);
};
getMsg(function(msg) {
console.log(msg);
})

同步API 异步API的区别(代码执行顺序)
同步API的代码执行顺序
同步API从上往下依次执行,前面代码会堵塞后面代码的执行
for(let i =0;i<10;i++){
console.log(i);
};
console.log('代码执行完毕');

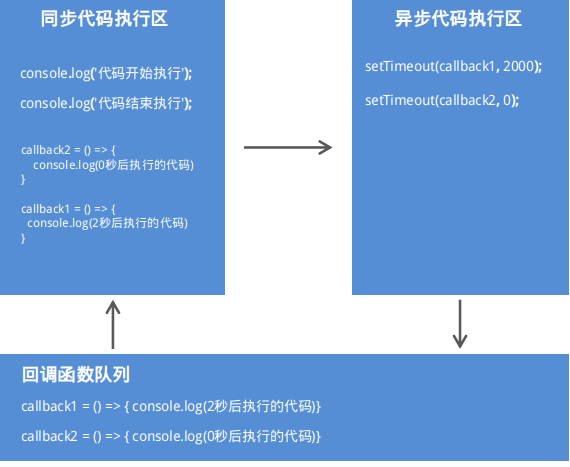
异步API的代码执行顺序
异步API不会等待API执行完毕后,再去执行下面的代码
console.log('代码执行完毕');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('0秒后执行的代码')
}, 0);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('2秒之后执行的代码');
}, 2000);
console.log('代码执行完毕');
Node.js中的异步API
Node.js中的异步API:读取文件 创建服务器对象,客户端发送请求均为异步API

Node.js中的回调地狱
回调函数嵌套着回调函数,被称为回调地狱,缺点:不易于维护。思考如下:后续代码执行完毕,但异步任务还没有执行完毕,该怎么解决呢
需求如下
依次读取A文件、B文件、C文件
//引进fs模块
const fs = require('fs');
//依次读取文件
fs.readFile('a.txt', 'utf8', (err, doc1) => {
console.log(1);
fs.readFile('b.txt', 'utf8', (err, doc2) => {
console.log(2);
fs.readFile('c.txt', 'utf8', (err, doc3) => {
console.log(3);
})
})
})

Node.js中的异步编程
Promise
Promise的出现,是为了解决Node.js中的回调地狱问题
里面有两个方法,resolve及reject,异步API执行成功后则调用resolve方法,异步API执行失败则调用reject方法,无论异步API执行成功或者失败,都会将异步API的结果传输到Promise的外面。
a.txt
hello Promisepromise.js
const fs = require('fs');
let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile('./a.txt', 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
// 如果异步API执行失败,则会调用reject方法
if (err != null) {
reject(err)
} else {
//如果异步API执行成功,则会执行resolve发布非法
resolve(doc)
}
})
})
//异步API执行成功,则会将信息打印在promise.then()方法
promise.then((doc) => {
console.log(doc);
})
//异步API执行失败,则会将错误信息打印在catch方法
.catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
})
promise来解决异步API依次执行的问题
//引进fs模块
const fs = require('fs')
//使用promise来解决异步API依次执行的问题
function p1() {
//必须要加return关键字 才能调用then方法
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile('./a.txt', 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
resolve(doc)
})
})
}
function p2() {
//必须要加return关键字 才能调用then方法
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile('./b.txt', 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
resolve(doc)
})
})
}
function p3() {
//必须要加return关键字 才能调用then方法
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fs.readFile('./c.txt', 'utf8', (err, doc) => {
resolve(doc)
})
})
}
p1().then((doc1) => {
console.log(doc1);
return p2()
}).then((doc2) => {
console.log(doc2);
return p3()
}).then((doc3) => {
console.log(doc3);
})
异步函数
异步函数是异步编程语法的终究解决方案,可以将异步代码写成同步的形式,让代码不再有回调函数嵌套,使代码变得清晰明了。
anysc关键字
1.普通函数定义前加async关键字,普通函数变成异步函数
2.异步函数默认返回promise对象
3.异步函数中使用return关键字进行结果返回,用return关键字代替resolve方法
4.异步函数中使用throw关键字抛出程序异常
5.调用异步函数链式中调用then方法获取异步函数的执行结果
6.调用异步函数链式中调用catch方法获取异步函数的执行的错误信息
async function fn() {
// throw '程序出错';
return '2020'
}
console.log(fn());
fn().then((doc) => {
console.log(doc);
}).catch((err) => {
console.log(err);
})
await关键字
1.await关键字只能出现在异步函数中
2.await后面只能写promise对象,写其它的类型是不可以的
3.await关键字暂停异步函数向下执行,直到promise返回结果。
async function p1() {
return 'p1'
}
async function p2() {
return 'p2'
}
async function p3() {
return 'p3'
}
async function run() {
let r1 = await p1();
let r2 = await p2();
let r3 = await p3();
console.log(r1);
console.log(r2);
console.log(r3);
}
run();

异步读取文件优化
const fs = require('fs');
//改造现有异步函数api 让其返回promise对象 从而支持异步函数语法
const promisify = require('util').promisify;
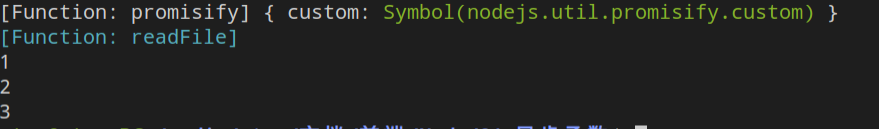
console.log(promisify);
//改变现有异步函数api,让其返回promise对象
const readFile = promisify(fs.readFile);
console.log(readFile);
async function run() {
let r1 = await readFile('./1.txt', 'utf8');
let r2 = await readFile('./2.txt', 'utf8');
let r3 = await readFile('./3.txt', 'utf8');
console.log(r1)
console.log(r2)
console.log(r3)
}
run()